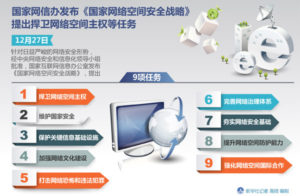
中央網信辦發布《國家網絡安全事件應急預案》
Communist Chinese Party issues National Network Security Incident Contingency Plans
2017年06月27日 17:16中国网信网
Notice of the Central Network Office on Printing and Distributing the Emergency Plan for National Network Security Incidents
China Network Office issued a document [2017] No. 4

Provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities, Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps Party Committee Network Security and Information Leading Group, the central and state organs of the ministries, the people’s organizations:
“National network security incident contingency plans” has been the central network security and information leading group agreed, is now issued to you, please carefully organize the implementation.
Central Network Security and Information Leading Group Office
January 10, 2017
National network security incident contingency plans
table of Contents
1 General
1.1 Purpose of preparation
1.2 Preparation basis
1.3 Scope of application
1.4 Event rating
1.5 working principle
Organizational Structure and Responsibilities
2.1 Leadership and Responsibilities
2.2 offices and responsibilities
2.3 Responsibilities of various departments
2.4 duties of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities)
3 monitoring and early warning
3.1 Early warning classification
3.2 Early warning monitoring
3.3 Early warning judgment and release
3.4 Early warning response
3.5 warning release
4 emergency treatment
4.1 Event report
4.2 Emergency response
4.3 Emergency end
5 Investigation and evaluation
6 to prevent work
6.1 Daily management
6.2 Walkthrough
6.3 Advocacy
6.4 Training
Precautions during important events
7 safeguards
7.1 Institutions and personnel
7.2 technical support team
7.3 expert team
7.4 Social resources
7.5 base platform
7.6 Technology research and development and industry promotion
7.7 International cooperation
7.8 material security
7.9 Funds protection
7.10 Responsibility and rewards and punishments
8 Annex
8.1 Project Management
8.2 Explanation of the plan
8.3 Implementation time of the plan
1 General
1.1 Purpose of preparation
Establish and improve the national network security incident emergency mechanism to improve the ability to deal with network security events, prevent and reduce network security incidents caused by the loss and harm, protect the public interest, safeguard national security, public safety and social order.
1.2 Preparation basis
“People’s Republic of China Incident Response Law”, “People’s Republic of China Network Security Law”, “National General Public Emergency Plan”, “Emergency Emergency Plan Management Measures” and “Information Security Technology Information Security Event Classification Classification Guide “(GB / Z 20986-2007) and other relevant provisions.
1.3 Scope of application
The cybersecurity incident referred to in this plan refers to events that cause adverse effects to the society due to human causes, hardware and software defects or failures, natural disasters, etc., which cause harm to the network and the information system or the data in it, Network attack events, information corruption events, information content security incidents, device facility failures, catastrophic events, and other events.
This plan applies to the work of network security events. Among them, the information content security incident response, to develop a special plan.
1.4 Event rating
Network security events are divided into four levels: particularly significant network security events, major network security incidents, larger network security events, and general network security events.
(1) meets one of the following scenarios for a particularly significant cyber security incident:
① Significant network and information systems suffer from particularly serious system losses, resulting in large paralysis of the system and loss of business processing capacity.
② State secret information, important sensitive information and key data loss or theft, tampering, counterfeiting, constitute a particularly serious threat to national security and social stability.
③ other network security incidents that pose a particularly serious threat to national security, social order, economic construction and public interest, causing particularly serious impact.
(2) meets one of the following scenarios and does not meet significant network security incidents for significant network security incidents:
① important network and information systems suffered serious system losses, resulting in a long time the system interrupted or partial paralysis, business processing capacity has been greatly affected.
② State secret information, important sensitive information and key data loss or theft, tampering, counterfeiting, posing a serious threat to national security and social stability.
③ other serious threats to national security, social order, economic construction and public interest, causing serious impact on network security incidents.
(3) meet one of the following conditions and does not meet significant network security incidents for larger network security events:
① important network and information systems suffer from greater system loss, resulting in system interruption, significantly affect the system efficiency, business processing capacity is affected.
② State secret information, important sensitive information and key data loss or theft, tampering, counterfeiting, posing a serious threat to national security and social stability.
③ other on the national security, social order, economic construction and public interests constitute a more serious threat, resulting in more serious impact of network security incidents.
(4) In addition to the above, the national security, social order, economic construction and public interests constitute a certain threat, resulting in a certain impact on the network security incidents for the general network security incidents.
1.5 working principle
Adhere to the unified leadership, grading responsibility; adhere to the unified command, close coordination, rapid response, scientific treatment; adhere to the prevention of prevention, prevention and emergency combination; adhere to who is responsible for who, who is responsible for running, give full play to all forces together Prevention and disposal of network security incidents.
Organizational Structure and Responsibilities
2.1 Leadership and Responsibilities
Under the leadership of the Central Network Security and Information Leading Group (hereinafter referred to as the “Leading Group”), the Office of the Central Network Security and Information Leading Group (hereinafter referred to as the “Central Network Office”) coordinates the organization of national network security incident response, Establish and improve the cross-sectoral linkage mechanism, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Public Security, the State Secrecy Bureau and other relevant departments in accordance with the division of responsibilities responsible for the relevant network security incident response. If necessary, the establishment of national network security incident emergency headquarters (hereinafter referred to as “the headquarters”), responsible for the special major network security incident handling organization and coordination and coordination.
2.2 offices and responsibilities
National Network Security Emergency Office (hereinafter referred to as “emergency office”) is located in the central network letter office, the specific work by the central network letter to do Network Security Coordination Bureau. Emergency Office is responsible for the network security emergency cross-sectoral, cross-regional coordination of the work and the headquarters of the transactional work, organization and guidance of national network security emergency technical support team to do emergency technical support work. The relevant departments are responsible for the relevant work of the Secretary-level comrades as liaison officers, contact emergency office work.
2.3 Responsibilities of various departments
The central and state departments and departments in accordance with their duties and authority, responsible for the sector, the industry network and information systems network security incident prevention, monitoring, reporting and emergency response.
2.4 duties of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities)
The administrative departments of the provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) shall coordinate and organize the prevention, monitoring, reporting and emergency handling of network security incidents in the regional network and information systems under the unified leadership of the Party Committee’s Network Safety and Information Leading Group.
3 monitoring and early warning
3.1 Early warning classification
The network security event warning level is divided into four levels: from high to low, followed by red, orange, yellow and blue, respectively, corresponding to occur or may occur particularly significant, significant, large and general network security events.
3.2 Early warning monitoring
The units in accordance with the “who is responsible for who is responsible for who who is responsible for” the requirements of the organization of the unit construction and operation of the network and information systems to carry out network security monitoring. Focus on industry executives or regulatory organizations to guide the organization to do the work of network security monitoring. The provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) network letter department with the actual situation in the region, the organization of the region to carry out the network and information systems security monitoring. Provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), the departments will be important monitoring information reported to be urgent, emergency office to carry out inter-provincial (district, city), cross-sectoral network security information sharing.
3.3 Early warning judgment and release
Provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities, departments of the monitoring of information on the judge, that the need for immediate preventive measures, should promptly notify the relevant departments and units, may occur on major and above network security incidents in a timely manner to the emergency response report. Provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), the departments can be based on monitoring and judging the situation, the release of the region, the industry’s orange and the following warning.
Emergency organization to determine, determine and publish red warning and involving multi-province (district, city), multi-sectoral, multi-industry early warning.
Early warning information includes the category of the event, the level of the alert, the starting time, the possible scope, the warning, the measures and time limits that should be taken, the issuing authority, and so on.
3.4 Early warning response
3.4.1 Red warning response
(1) the emergency response organization organization early warning response work, contact experts and relevant agencies, organizations to track the development of the situation to study and formulate preventive measures and emergency work program, coordination of resource scheduling and departmental linkage of the preparatory work.
(2) the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), the Department of network security incident emergency command agencies to implement 24 hours on duty, the relevant personnel to maintain communication links. Strengthen the network security incident monitoring and development of information collection work, organize and guide the emergency support team, the relevant operating units to carry out emergency treatment or preparation, risk assessment and control work, the important situation retribution urgent.
(3) the national network security emergency technical support team into the standby state, for the early warning information research to develop a response program, check emergency vehicles, equipment, software tools, to ensure a good condition.
3.4.2 Orange warning response
(1) the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departmental network security incident emergency command agencies to start the corresponding contingency plans, organize early warning response, do risk assessment, emergency preparedness and risk control.
(2) the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments in a timely manner to the situation of the situation reported to the emergency response. The Emergency Office is closely following the development of the matter and timely notification of the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) and departments.
(3) the national network security emergency technical support team to keep in touch, check emergency vehicles, equipment, software tools, to ensure that in good condition.
3.4.3 yellow, blue warning response
The relevant regional and departmental network security incident emergency command agencies to start the corresponding contingency plans to guide the organization to carry out early warning response.
3.5 warning release
Early warning release departments or regions according to the actual situation, to determine whether to lift the warning, timely release warning release information.
4 emergency treatment
4.1 Event report
After the network security incident occurs, the incident unit should immediately start the emergency plan, the implementation of disposal and timely submission of information. The relevant regions and departments immediately organize the early disposal, control the situation, eliminate hidden dangers, at the same time organization and judgment, pay attention to save the evidence, do a good job of information communication. For the primary judgment is particularly significant, major network security incidents, and immediately report to the emergency office.
4.2 Emergency response
The network security incident emergency response is divided into four levels, corresponding to particularly significant, significant, large and general network security events. Level I is the highest response level.
4.2.1 Class I response
Is a particularly important network security incidents, timely start I-level response, the establishment of the headquarters, the implementation of emergency response to the unified leadership, command and coordination responsibilities. Emergency Office 24 hours on duty.
The relevant departments (district, city), the department emergency response agencies into the emergency state, in the command of the unified leadership, command and coordination, responsible for the province (district, city), the department emergency work or support security work, 24 hours on duty, And sent to participate in emergency office work.
The relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments to track the development of the situation, check the scope of the impact of the situation in time to change the situation, the progress of the report retribution. The headquarters of the response to the work of the decision-making arrangements, the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) and departments responsible for the organization and implementation.
4.2.2 Class II response
The level response of the network security incident is determined by the relevant province (district, city) and the department according to the nature and circumstances of the incident.
(1) the incident occurred in the province (district, city) or department of the emergency command agencies into the emergency state, in accordance with the relevant emergency plans to do emergency work.
(2) the incident occurred in the province (district, city) or departments in a timely manner to change the situation developments. The emergency office will keep the relevant matters and the relevant departments and departments in a timely manner.
(3) the disposal of the need for other relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments and national network security emergency technical support team with the support and business emergency response to be coordinated. Relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments and national network security emergency technical support team should be based on their respective responsibilities, and actively cooperate to provide support.
(4) The relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) and departments shall, in accordance with the notification of the emergency office, strengthen the prevention and prevent the greater impact and losses on the basis of their actual and targeted efforts.
4.2.3 Class Ⅲ, Ⅳ level response
Event areas and departments in accordance with the relevant plans for emergency response.
4.3 Emergency end
4.3.1 End of class I response
Emergency Office to make recommendations, reported to the headquarters after approval, timely notification of the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) and departments.
4.3.2 Level II response ends
(Autonomous regions and municipalities) or departments, the emergency response, emergency response to the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) and departments.
5 Investigation and evaluation
Special major network security incidents by the emergency branch of the relevant departments and provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) to investigate and summarize the assessment, according to the procedures reported. Significant and the following network security incidents are organized by the event area or department to organize their own investigation and summary assessment, including the major network security incident related to the summary report of the report retribution. Summary of the investigation report should be the cause of the event, nature, impact, responsibility analysis and evaluation, put forward the views and improvement measures.
The investigation and summary of the incident is carried out in principle within 30 days after the end of the emergency response.
6 to prevent work
6.1 Daily management
All localities and departments should do a good job in the day-to-day prevention of network security incidents, formulate and improve relevant emergency plans, do a good job of network security inspection, risk investigation, risk assessment and disaster recovery, improve the network security information notification mechanism, take timely and effective measures, Reduce and avoid the occurrence and harm of network security incidents, improve the ability to deal with network security incidents.
6.2 Walkthrough
Central Network letter to coordinate the relevant departments to organize regular exercises, test and improve the plan to improve the actual combat capability.
The provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments at least once a year to organize a plan exercise, and the exercise situation reported to the central network letter to do.
6.3 Advocacy
All localities and departments should make full use of various media and other effective propaganda forms to strengthen the publicity and disposal of relevant laws, regulations and policies for the prevention and disposal of sudden network security incidents and carry out propaganda activities on basic knowledge and skills of network security.
6.4 Training
All localities and departments should regard the emergency knowledge of cyber security incidents as the training content of leading cadres and relevant personnel, strengthen the training of network security, especially network security contingency plans, and improve awareness and skills.
Precautions during important events
In the national important activities, during the meeting, the provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), various departments to strengthen the network security incidents to prevent and emergency response to ensure network security. Emergency Office to coordinate the work of network security, according to the requirements of the relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments to start the red warning response. The relevant provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments to strengthen network security monitoring and analysis of judgments, timely warning may cause significant impact on the risks and risks, key departments, key positions to maintain 24 hours on duty, timely detection and disposal of network security incidents.
7 safeguards
7.1 Institutions and personnel
All localities and departments, units to implement the network security emergency work responsibility system, the responsibility to implement specific departments, specific positions and individuals, and establish a sound emergency working mechanism.
7.2 technical support team
Strengthen the network security emergency technical support team building, do a good job of network security incident monitoring and early warning, prevention and protection, emergency response, emergency technical support work. Support network security enterprises to improve emergency response capabilities, to provide emergency technical support. The central network to do assessment of the development of accreditation standards, organizational assessment and identification of national network security emergency technical support team. All provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments should be equipped with the necessary network security professional and technical personnel, and strengthen the national network security related technical units of communication, coordination, the establishment of the necessary network security information sharing mechanism.
7.3 expert team
The establishment of national network security emergency expert group, for the network security incident prevention and disposal of technical advice and decision-making recommendations. All regions and departments to strengthen their own team of experts, give full play to the role of experts in the emergency response.
7.4 Social resources
From the educational research institutions, enterprises and institutions, associations in the selection of network security personnel, pooling technology and data resources, the establishment of network security incident emergency service system to improve the response to particularly significant, major network security incidents.
7.5 base platform
All regions and departments to strengthen the network security platform and management platform for emergency management, so early detection, early warning, early response, improve emergency response capability.
7.6 Technology research and development and industry promotion
Relevant departments to strengthen network security technology research, and constantly improve the technical equipment, emergency response to provide technical support. Strengthen the policy guidance, focus on supporting network security monitoring and early warning, prevention and protection, disposal of rescue, emergency services and other directions to enhance the overall level of network security industry and core competitiveness, and enhance the prevention and disposal of network security event industry support capabilities.
7.7 International cooperation
Relevant departments to establish international cooperation channels, signed a cooperation agreement, if necessary, through international cooperation to deal with sudden network security incidents.
7.8 material security
Strengthen the network security emergency equipment, tools, reserves, timely adjustment, upgrade software hardware tools, and constantly enhance the emergency technical support capabilities.
7.9 Funds protection
The financial department provides the necessary financial guarantee for the emergency disposal of the network security incident. Relevant departments to use the existing policies and funding channels to support the network security emergency technical support team building, expert team building, basic platform construction, technology research and development, planning exercises, material security and other work carried out. All regions and departments for the network security emergency work to provide the necessary financial protection.
7.10 Responsibility and rewards and punishments
Implementation of Responsibility System for Emergency Work of Network Security Incident.
The central network letter office and the relevant regional and departmental network security incident emergency management work to make outstanding contributions to the advanced collective and individuals to commend and reward.
The central network and the relevant departments and departments do not follow the provisions of the formulation of plans and organizations to carry out exercises, late, false, concealed and owe the network security incidents important or emergency management work in other misconduct, dereliction of duty, in accordance with the relevant Provides for the responsible person to be punished; constitute a crime, shall be held criminally responsible.
8 Annex
8.1 Project Management
The plan is evaluated in principle once a year and revised in a timely manner according to the actual situation. The revision work is handled by the central network.
All provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), departments and units shall, according to the plan, formulate or revise the contingency plans for the network security incidents in the region, the department, the industry and the unit.
8.2 Explanation of the plan
The plan is interpreted by the central network letter office.
8.3 Implementation time of the plan
The plan has been implemented since the date of issuance.
Attachment:
1. Network security event classification
2. Terminology
3. Network and information system loss degree description
attachment1
Network Security Event Classification
Network security events are classified as unwanted program events, network attack events, information corruption events, information content security incidents, device facility failures, catastrophic events, and other network security incidents.
(1) Harmful program events are classified into computer virus events, worm events, Trojan events, botnet events, mixed program attack events, web embedded malicious code events, and other unwanted program events.
(2) network attacks are divided into denial of service attacks, backdoor attacks, vulnerability attacks, network scanning eavesdropping events, phishing events, interference events and other network attacks.
(3) information destruction events are classified as information tampering events, information fake events, information disclosure incidents, information theft events, information loss events and other information destruction events.
(4) Information content security incidents refer to the dissemination of laws and regulations through the Internet to prohibit information, organize illegal series, incite rallies or hype sensitive issues and endanger national security, social stability and public interest events.
(5) equipment and equipment failure is divided into hardware and software failure, peripheral protection facilities failure, man-made damage and other equipment and equipment failure.
(6) Disastrous events refer to network security incidents caused by other emergencies such as natural disasters.
(7) Other events refer to network security events that can not be classified as above.
Annex 2
Terminology
First, the important network and information systems
The network and information systems that are closely related to national security, social order, economic construction and public interest.
(Reference: “Information Security Technology Information Security Event Classification and Classification Guide” (GB / Z 20986-2007))
Second, the important sensitive information
Information that is not related to national secrets but is closely related to national security, economic development, social stability and corporate and public interest, which, once unauthorized, is disclosed, lost, misused, tampered with or destroyed, may have the following consequences:
A) damage to national defense, international relations;
B) damage to State property, public interest and personal property or personal safety;
C) affect the state to prevent and combat economic and military spies, political infiltration, organized crime;
D) affect the administrative organs to investigate and deal with illegal, dereliction of duty, or suspected of illegal, dereliction of duty;
E) interfere with government departments to carry out administrative activities such as supervision, management, inspection and auditing impartially, hinder government departments from performing their duties;
F) endanger the national key infrastructure, government information system security;
G) affect the market order, resulting in unfair competition, undermining the laws of the market;
H) can be inferred from the state secret matter;
I) infringement of personal privacy, corporate trade secrets and intellectual property rights;
J) damage to the country, business, personal other interests and reputation.
(Reference: “Information Security Technology Cloud Computing Service Security Guide” (GB / T31167-2014))
Annex 3
Network and Information System Losses
Network and information system loss refers to the network security incidents due to network hardware and software, functions and data damage, resulting in system business interruption, so as to the loss caused by the organization, the size of the main consideration to restore the normal operation of the system and eliminate security incidents Negative effects are deducted as particularly serious system losses, severe system losses, greater system losses, and minor system losses, as follows:
A) Particularly serious systemic damage: a large area of paralysis of the system, loss of business processing capacity, or confidentiality, integrity, availability of critical data, serious damage to the system, normal operation of the system and elimination of the negative impact of security incidents The price paid is very great, for the incident is unbearable;
B) Serious system loss: causing the system to be interrupted for a long time or partially paralyzed, greatly compromising its business processing capacity, or the confidentiality, integrity, availability of the critical data, the recovery of the system and the elimination of security incidents Negative effects are huge, but are affordable for the organization;
C) Larger system losses: causing system outages, significantly affecting system efficiency, affecting the operational capacity of important information systems or general information systems, or the confidentiality, integrity, availability of system critical data, and the restoration of the system The cost of running and eliminating the negative effects of security incidents is greater, but it is entirely affordable for the organization;
D) Smaller system losses: causing system interruption, affecting system efficiency, affecting system operational capacity, or confidentiality, integrity, availability of system critical data, restoring system uptime and eliminating security incidents The cost of the impact is less.
Original Mandarin Chinese:
中央網信辦關於印發《國家網絡安全事件應急預案》的通知
中網辦發文〔2017〕4號

各省、自治區、直轄市、新疆生產建設兵團黨委網絡安全和信息化領導小組,中央和國家機關各部委、各人民團體:
《國家網絡安全事件應急預案》已經中央網絡安全和信息化領導小組同意,現印發給你們,請認真組織實施。
中央網絡安全和信息化領導小組辦公室
2017年1月10日
國家網絡安全事件應急預案
目 錄
1 總則
1.1 編制目的
1.2 編制依據
1.3 適用範圍
1.4 事件分級
1.5 工作原則
2 組織機構與職責
2.1 領導機構與職責
2.2 辦事機構與職責
2.3 各部門職責
2.4 各省(區、市)職責
3 監測與預警
3.1 預警分級
3.2 預警監測
3.3 預警研判和發布
3.4 預警響應
3.5 預警解除
4 應急處置
4.1 事件報告
4.2 應急響應
4.3 應急結束
5 調查與評估
6 預防工作
6.1 日常管理
6.2 演練
6.3 宣傳
6.4 培訓
6.5 重要活動期間的預防措施
7 保障措施
7.1 機構和人員
7.2 技術支撐隊伍
7.3 專家隊伍
7.4 社會資源
7.5 基礎平台
7.6 技術研發和產業促進
7.7 國際合作
7.8 物資保障
7.9 經費保障
7.10 責任與獎懲
8 附則
8.1 預案管理
8.2 預案解釋
8.3 預案實施時間
1 總則
1.1 編制目的
建立健全國家網絡安全事件應急工作機制,提高應對網絡安全事件能力,預防和減少網絡安全事件造成的損失和危害,保護公眾利益,維護國家安全、公共安全和社會秩序。
1.2 編制依據
《中華人民共和國突發事件應對法》、《中華人民共和國網絡安全法》、《國家突發公共事件總體應急預案》、《突發事件應急預案管理辦法》和《信息安全技術信息安全事件分類分級指南》(GB/Z 20986-2007)等相關規定。
1.3 適用範圍
本預案所指網絡安全事件是指由於人為原因、軟硬件缺陷或故障、自然災害等,對網絡和信息系統或者其中的數據造成危害,對社會造成負面影響的事件,可分為有害程序事件、網絡攻擊事件、信息破壞事件、信息內容安全事件、設備設施故障、災害性事件和其他事件。
本預案適用於網絡安全事件的應對工作。其中,有關信息內容安全事件的應對,另行製定專項預案。
1.4 事件分級
網絡安全事件分為四級:特別重大網絡安全事件、重大網絡安全事件、較大網絡安全事件、一般網絡安全事件。
(1)符合下列情形之一的,為特別重大網絡安全事件:
①重要網絡和信息系統遭受特別嚴重的系統損失,造成系統大面積癱瘓,喪失業務處理能力。
②國家秘密信息、重要敏感信息和關鍵數據丟失或被竊取、篡改、假冒,對國家安全和社會穩定構成特別嚴重威脅。
③其他對國家安全、社會秩序、經濟建設和公眾利益構成特別嚴重威脅、造成特別嚴重影響的網絡安全事件。
(2)符合下列情形之一且未達到特別重大網絡安全事件的,為重大網絡安全事件:
①重要網絡和信息系統遭受嚴重的系統損失,造成系統長時間中斷或局部癱瘓,業務處理能力受到極大影響。
②國家秘密信息、重要敏感信息和關鍵數據丟失或被竊取、篡改、假冒,對國家安全和社會穩定構成嚴重威脅。
③其他對國家安全、社會秩序、經濟建設和公眾利益構成嚴重威脅、造成嚴重影響的網絡安全事件。
(3)符合下列情形之一且未達到重大網絡安全事件的,為較大網絡安全事件:
①重要網絡和信息系統遭受較大的系統損失,造成系統中斷,明顯影響系統效率,業務處理能力受到影響。
②國家秘密信息、重要敏感信息和關鍵數據丟失或被竊取、篡改、假冒,對國家安全和社會穩定構成較嚴重威脅。
③其他對國家安全、社會秩序、經濟建設和公眾利益構成較嚴重威脅、造成較嚴重影響的網絡安全事件。
(4)除上述情形外,對國家安全、社會秩序、經濟建設和公眾利益構成一定威脅、造成一定影響的網絡安全事件,為一般網絡安全事件。
1.5 工作原則
堅持統一領導、分級負責;堅持統一指揮、密切協同、快速反應、科學處置;堅持預防為主,預防與應急相結合;堅持誰主管誰負責、誰運行誰負責,充分發揮各方面力量共同做好網絡安全事件的預防和處置工作。
2 組織機構與職責
2.1 領導機構與職責
在中央網絡安全和信息化領導小組(以下簡稱“領導小組”)的領導下,中央網絡安全和信息化領導小組辦公室(以下簡稱“中央網信辦”)統籌協調組織國家網絡安全事件應對工作,建立健全跨部門聯動處置機制,工業和信息化部、公安部、國家保密局等相關部門按照職責分工負責相關網絡安全事件應對工作。必要時成立國家網絡安全事件應急指揮部(以下簡稱“指揮部”),負責特別重大網絡安全事件處置的組織指揮和協調。
2.2 辦事機構與職責
國家網絡安全應急辦公室(以下簡稱“應急辦”)設在中央網信辦,具體工作由中央網信辦網絡安全協調局承擔。應急辦負責網絡安全應急跨部門、跨地區協調工作和指揮部的事務性工作,組織指導國家網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍做好應急處置的技術支撐工作。有關部門派負責相關工作的司局級同志為聯絡員,聯絡應急辦工作。
2.3 各部門職責
中央和國家機關各部門按照職責和權限,負責本部門、本行業網絡和信息系統網絡安全事件的預防、監測、報告和應急處置工作。
2.4 各省(區、市)職責
各省(區、市)網信部門在本地區黨委網絡安全和信息化領導小組統一領導下,統籌協調組織本地區網絡和信息系統網絡安全事件的預防、監測、報告和應急處置工作。
3 監測與預警
3.1 預警分級
網絡安全事件預警等級分為四級:由高到低依次用紅色、橙色、黃色和藍色表示,分別對應發生或可能發生特別重大、重大、較大和一般網絡安全事件。
3.2 預警監測
各單位按照“誰主管誰負責、誰運行誰負責”的要求,組織對本單位建設運行的網絡和信息系統開展網絡安全監測工作。重點行業主管或監管部門組織指導做好本行業網絡安全監測工作。各省(區、市)網信部門結合本地區實際,統籌組織開展對本地區網絡和信息系統的安全監測工作。各省(區、市)、各部門將重要監測信息報應急辦,應急辦組織開展跨省(區、市)、跨部門的網絡安全信息共享。
3.3 預警研判和發布
各省(區、市)、各部門組織對監測信息進行研判,認為需要立即採取防範措施的,應當及時通知有關部門和單位,對可能發生重大及以上網絡安全事件的信息及時向應急辦報告。各省(區、市)、各部門可根據監測研判情況,發布本地區、本行業的橙色及以下預警。
應急辦組織研判,確定和發布紅色預警和涉及多省(區、市)、多部門、多行業的預警。
預警信息包括事件的類別、預警級別、起始時間、可能影響範圍、警示事項、應採取的措施和時限要求、發布機關等。
3.4 預警響應
3.4.1 紅色預警響應
(1)應急辦組織預警響應工作,聯繫專家和有關機構,組織對事態發展情況進行跟踪研判,研究制定防範措施和應急工作方案,協調組織資源調度和部門聯動的各項準備工作。
(2)有關省(區、市)、部門網絡安全事件應急指揮機構實行24小時值班,相關人員保持通信聯絡暢通。加強網絡安全事件監測和事態發展信息蒐集工作,組織指導應急支撐隊伍、相關運行單位開展應急處置或準備、風險評估和控制工作,重要情況報應急辦。
(3)國家網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍進入待命狀態,針對預警信息研究制定應對方案,檢查應急車輛、設備、軟件工具等,確保處於良好狀態。
3.4.2 橙色預警響應
(1)有關省(區、市)、部門網絡安全事件應急指揮機構啟動相應應急預案,組織開展預警響應工作,做好風險評估、應急準備和風險控制工作。
(2)有關省(區、市)、部門及時將事態發展情況報應急辦。應急辦密切關注事態發展,有關重大事項及時通報相關省(區、市)和部門。
(3)國家網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍保持聯絡暢通,檢查應急車輛、設備、軟件工具等,確保處於良好狀態。
3.4.3 黃色、藍色預警響應
有關地區、部門網絡安全事件應急指揮機構啟動相應應急預案,指導組織開展預警響應。
3.5 預警解除
預警發布部門或地區根據實際情況,確定是否解除預警,及時發布預警解除信息。
4 應急處置
4.1 事件報告
網絡安全事件發生後,事發單位應立即啟動應急預案,實施處置並及時報送信息。各有關地區、部門立即組織先期處置,控制事態,消除隱患,同時組織研判,注意保存證據,做好信息通報工作。對於初判為特別重大、重大網絡安全事件的,立即報告應急辦。
4.2 應急響應
網絡安全事件應急響應分為四級,分別對應特別重大、重大、較大和一般網絡安全事件。 I級為最高響應級別。
4.2.1 Ⅰ級響應
屬特別重大網絡安全事件的,及時啟動I級響應,成立指揮部,履行應急處置工作的統一領導、指揮、協調職責。應急辦24小時值班。
有關省(區、市)、部門應急指揮機構進入應急狀態,在指揮部的統一領導、指揮、協調下,負責本省(區、市)、本部門應急處置工作或支援保障工作,24小時值班,並派員參加應急辦工作。
有關省(區、市)、部門跟踪事態發展,檢查影響範圍,及時將事態發展變化情況、處置進展情況報應急辦。指揮部對應對工作進行決策部署,有關省(區、市)和部門負責組織實施。
4.2.2 Ⅱ級響應
網絡安全事件的Ⅱ級響應,由有關省(區、市)和部門根據事件的性質和情況確定。
(1)事件發生省(區、市)或部門的應急指揮機構進入應急狀態,按照相關應急預案做好應急處置工作。
(2)事件發生省(區、市)或部門及時將事態發展變化情況報應急辦。應急辦將有關重大事項及時通報相關地區和部門。
(3)處置中需要其他有關省(區、市)、部門和國家網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍配合和支持的,商應急辦予以協調。相關省(區、市)、部門和國家網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍應根據各自職責,積極配合、提供支持。
(4)有關省(區、市)和部門根據應急辦的通報,結合各自實際有針對性地加強防範,防止造成更大範圍影響和損失。
4.2.3 Ⅲ級、Ⅳ級響應
事件發生地區和部門按相關預案進行應急響應。
4.3 應急結束
4.3.1 Ⅰ級響應結束
應急辦提出建議,報指揮部批准後,及時通報有關省(區、市)和部門。
4.3.2 Ⅱ級響應結束
由事件發生省(區、市)或部門決定,報應急辦,應急辦通報相關省(區、市)和部門。
5 調查與評估
特別重大網絡安全事件由應急辦組織有關部門和省(區、市)進行調查處理和總結評估,並按程序上報。重大及以下網絡安全事件由事件發生地區或部門自行組織調查處理和總結評估,其中重大網絡安全事件相關總結調查報告報應急辦。總結調查報告應對事件的起因、性質、影響、責任等進行分析評估,提出處理意見和改進措施。
事件的調查處理和總結評估工作原則上在應急響應結束後30天內完成。
6 預防工作
6.1 日常管理
各地區、各部門按職責做好網絡安全事件日常預防工作,制定完善相關應急預案,做好網絡安全檢查、隱患排查、風險評估和容災備份,健全網絡安全信息通報機制,及時採取有效措施,減少和避免網絡安全事件的發生及危害,提高應對網絡安全事件的能力。
6.2 演練
中央網信辦協調有關部門定期組織演練,檢驗和完善預案,提高實戰能力。
各省(區、市)、各部門每年至少組織一次預案
,並將演練情況報中央網信辦。
6.3 宣傳
各地區、各部門應充分利用各種傳播媒介及其他有效的宣傳形式,加強突發網絡安全事件預防和處置的有關法律、法規和政策的宣傳,開展網絡安全基本知識和技能的宣傳活動。
6.4 培訓
各地區、各部門要將網絡安全事件的應急知識列為領導幹部和有關人員的培訓內容,加強網絡安全特別是網絡安全應急預案的培訓,提高防範意識及技能。
6.5 重要活動期間的預防措施
在國家重要活動、會議期間,各省(區、市)、各部門要加強網絡安全事件的防範和應急響應,確保網絡安全。應急辦統籌協調網絡安全保障工作,根據需要要求有關省(區、市)、部門啟動紅色預警響應。有關省(區、市)、部門加強網絡安全監測和分析研判,及時預警可能造成重大影響的風險和隱患,重點部門、重點崗位保持24小時值班,及時發現和處置網絡安全事件隱患。
7 保障措施
7.1 機構和人員
各地區、各部門、各單位要落實網絡安全應急工作責任制,把責任落實到具體部門、具體崗位和個人,並建立健全應急工作機制。
7.2 技術支撐隊伍
加強網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍建設,做好網絡安全事件的監測預警、預防防護、應急處置、應急技術支援工作。支持網絡安全企業提升應急處置能力,提供應急技術支援。中央網信辦製定評估認定標準,組織評估和認定國家網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍。各省(區、市)、各部門應配備必要的網絡安全專業技術人才,並加強與國家網絡安全相關技術單位的溝通、協調,建立必要的網絡安全信息共享機制。
7.3 專家隊伍
建立國家網絡安全應急專家組,為網絡安全事件的預防和處置提供技術諮詢和決策建議。各地區、各部門加強各自的專家隊伍建設,充分發揮專家在應急處置工作中的作用。
7.4 社會資源
從教育科研機構、企事業單位、協會中選拔網絡安全人才,匯集技術與數據資源,建立網絡安全事件應急服務體系,提高應對特別重大、重大網絡安全事件的能力。
7.5 基礎平台
各地區、各部門加強網絡安全應急基礎平台和管理平台建設,做到早發現、早預警、早響應,提高應急處置能力。
7.6 技術研發和產業促進
有關部門加強網絡安全防範技術研究,不斷改進技術裝備,為應急響應工作提供技術支撐。加強政策引導,重點支持網絡安全監測預警、預防防護、處置救援、應急服務等方向,提升網絡安全應急產業整體水平與核心競爭力,增強防範和處置網絡安全事件的產業支撐能力。
7.7 國際合作
有關部門建立國際合作渠道,簽訂合作協定,必要時通過國際合作共同應對突發網絡安全事件。
7.8 物資保障
加強對網絡安全應急裝備、工具的儲備,及時調整、升級軟件硬件工具,不斷增強應急技術支撐能力。
7.9 經費保障
財政部門為網絡安全事件應急處置提供必要的資金保障。有關部門利用現有政策和資金渠道,支持網絡安全應急技術支撐隊伍建設、專家隊伍建設、基礎平台建設、技術研發、預案演練、物資保障等工作開展。各地區、各部門為網絡安全應急工作提供必要的經費保障。
7.10 責任與獎懲
網絡安全事件應急處置工作實行責任追究制。
中央網信辦及有關地區和部門對網絡安全事件應急管理工作中作出突出貢獻的先進集體和個人給予表彰和獎勵。
中央網信辦及有關地區和部門對不按照規定制定預案和組織開展演練,遲報、謊報、瞞報和漏報網絡安全事件重要情況或者應急管理工作中有其他失職、瀆職行為的,依照相關規定對有關責任人給予處分;構成犯罪的,依法追究刑事責任。
8 附則
8.1 預案管理
本預案原則上每年評估一次,根據實際情況適時修訂。修訂工作由中央網信辦負責。
各省(區、市)、各部門、各單位要根據本預案製定或修訂本地區、本部門、本行業、本單位網絡安全事件應急預案。
8.2 預案解釋
本預案由中央網信辦負責解釋。
8.3 預案實施時間
本預案自印發之日起實施。
附件:
1. 網絡安全事件分類
2. 名詞術語
3. 網絡和信息系統損失程度劃分說明
附件1
網絡安全事件分類
網絡安全事件分為有害程序事件、網絡攻擊事件、信息破壞事件、信息內容安全事件、設備設施故障、災害性事件和其他網絡安全事件等。
(1)有害程序事件分為計算機病毒事件、蠕蟲事件、特洛伊木馬事件、殭屍網絡事件、混合程序攻擊事件、網頁內嵌惡意代碼事件和其他有害程序事件。
(2)網絡攻擊事件分為拒絕服務攻擊事件、後門攻擊事件、漏洞攻擊事件、網絡掃描竊聽事件、網絡釣魚事件、干擾事件和其他網絡攻擊事件。
(3)信息破壞事件分為信息篡改事件、信息假冒事件、信息洩露事件、信息竊取事件、信息丟失事件和其他信息破壞事件。
(4)信息內容安全事件是指通過網絡傳播法律法規禁止信息,組織非法串聯、煽動集會遊行或炒作敏感問題並危害國家安全、社會穩定和公眾利益的事件。
(5)設備設施故障分為軟硬件自身故障、外圍保障設施故障、人為破壞事故和其他設備設施故障。
(6)災害性事件是指由自然災害等其他突發事件導致的網絡安全事件。
(7)其他事件是指不能歸為以上分類的網絡安全事件。
附件2
名詞術語
一、重要網絡與信息系統
所承載的業務與國家安全、社會秩序、經濟建設、公眾利益密切相關的網絡和信息系統。
(參考依據:《信息安全技術信息安全事件分類分級指南》(GB/Z 20986-2007))
二、重要敏感信息
不涉及國家秘密,但與國家安全、經濟發展、社會穩定以及企業和公眾利益密切相關的信息,這些信息一旦未經授權披露、丟失、濫用、篡改或銷毀,可能造成以下後果:
a) 損害國防、國際關係;
b) 損害國家財產、公共利益以及個人財產或人身安全;
c) 影響國家預防和打擊經濟與軍事間諜、政治滲透、有組織犯罪等;
d) 影響行政機關依法調查處理違法、瀆職行為,或涉嫌違法、瀆職行為;
e) 干擾政府部門依法公正地開展監督、管理、檢查、審計等行政活動,妨礙政府部門履行職責;
f) 危害國家關鍵基礎設施、政府信息系統安全;
g) 影響市場秩序,造成不公平競爭,破壞市場規律;
h) 可推論出國家秘密事項;
i) 侵犯個人隱私、企業商業秘密和知識產權;
j) 損害國家、企業、個人的其他利益和聲譽。
(參考依據:《信息安全技術雲計算服務安全指南》(GB/T31167-2014))
附件3
網絡和信息系統損失程度劃分說明
網絡和信息系統損失是指由於網絡安全事件對系統的軟硬件、功能及數據的破壞,導致系統業務中斷,從而給事發組織所造成的損失,其大小主要考慮恢復系統正常運行和消除安全事件負面影響所需付出的代價,劃分為特別嚴重的系統損失、嚴重的系統損失、較大的系統損失和較小的系統損失,說明如下:
a) 特別嚴重的系統損失:造成系統大面積癱瘓,使其喪失業務處理能力,或系統關鍵數據的保密性、完整性、可用性遭到嚴重破壞,恢復系統正常運行和消除安全事件負面影響所需付出的代價十分巨大,對於事發組織是不可承受的;
b) 嚴重的系統損失:造成系統長時間中斷或局部癱瘓,使其業務處理能力受到極大影響,或系統關鍵數據的保密性、完整性、可用性遭到破壞,恢復系統正常運行和消除安全事件負面影響所需付出的代價巨大,但對於事發組織是可承受的;
c) 較大的系統損失:造成系統中斷,明顯影響系統效率,使重要信息系統或一般信息系統業務處理能力受到影響,或系統重要數據的保密性、完整性、可用性遭到破壞,恢復系統正常運行和消除安全事件負面影響所需付出的代價較大,但對於事發組織是完全可以承受的;
d) 較小的系統損失:造成系統短暫中斷,影響系統效率,使系統業務處理能力受到影響,或系統重要數據的保密性、完整性、可用性遭到影響,恢復系統正常運行和消除安全事件負面影響所需付出的代價較小。
Original referring URL:
http://www.cac.gov.cn/2017-06/27/c_1121220113.htm