Chinese Military Electromagnetic Spectrum Technology Determines the Future Development of Defeating the US at War
For a long time, in order to solve the A2/AD dilemma and achieve a new offset strategy, the U.S. has launched combat operations such as open space/air-sea warfare, cyber-centric warfare, distributed killing, multi-domain warfare, and mixed warfare. With new ideas, we constantly seek military advantages such as missile offensive and defense, cyber-electromagnetics, and multi-domain space. Today, the electromagnetic spectrum war has become the new darling of leading a new round of military theory and technological innovation. Researching and analyzing the status quo and characteristics of the development of the US military’s electromagnetic spectrum combat has important practical significance for our military’s success in defeating the enemy in the information battlefield.
1 Development of Electromagnetic Spectrum Warfare
In 1956, Admiral Sergei Gorschkov, the former Soviet naval commander, pointed out: “Who controls the electromagnetic spectrum, who will win the next war.” Sixty years later, the electromagnetic spectrum has become one of the key battlefields of modern warfare. In order to compete for the advantages of the electromagnetic spectrum in the battlefield, the US military conducted in-depth explorations from combat theory to equipment technology and developed rapidly.
1.1 Evolution of theory
Electromagnetic spectrum control has a long history. In the early 1970s, Thomas H, chairman of the US Senate Association. Moorer said that the winner of World War III will be a party that can highly control and manage the electromagnetic spectrum. The United States “Old Ravens” Association first proposed the use of electromagnetic control (EMC) as the fourth component of the concept of electronic warfare. In 2009, Strategic Command launched the early concept of electromagnetic spectrum warfare (EMSW), and added tasks such as electromagnetic spectrum management (EMSM), electromagnetic spectrum control (EMSC), and electromagnetic battle control (EMBC) on the basis of electronic warfare [1]. In 2012, the Strategic Command established the Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Control Center (JEMSCC) to achieve full integration of electronic warfare and electromagnetic spectrum management, and each of the units also established corresponding organizational coordination agencies and detachments [2]. In the same year, the US Navy proposed the concept of Electromagnetic Maneuver Warfare (EMMW) [3], and in March 2015 released the “21st Century Maritime Force Cooperation Strategy,” which outlines the goals, components, technology projects, and implementation paths of the electromagnetic maneuver warfare [4]. In December 2015, Terry Halvorsen, chief information officer of the US Department of Defense, pointed out that the electromagnetic spectrum is expected to be considered as the sixth battlefield following land, sea, air, space, and cyberspace [5]; in the same month, the Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments Defining Electromagnetic Waves: Regaining U.S. Dominance in the Electromagnetic Spectrum Field[6] The report proposes the concept of “low-zero-power” electromagnetic spectrum warfare, expounding concept ideas, trend features, capabilities and technical requirements and current obstacles, and presenting views, concepts, Procurement, technical, verification, etc. At the end of November 2016, the 53rd International Conference of the “Old Ravens” Association of the United States took the theme “Global Vision of Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations” as the theme to demonstrate the new concepts and technical achievements of electronic warfare, spectrum sensing and conflict resolution, and explored the electromagnetic spectrum operational environment. Policy regulations, equipment procurement, joint training and combat capabilities, etc. [7]. In January 2017, the new Secretary of Defense Ashton Carter signed the first “Electronic Warfare Strategy” document, officially establishing the electromagnetic spectrum as an independent operational domain and elaborating on how to conduct operations [8].
1.2 Policies and Orders
Strategic policies and military doctrines reflect the development of the US military’s combat theory. From 2006 to 2014, the US Department of Defense updated the “Electromagnetic Spectrum Strategy” to focus on advancing strategic objectives such as development of spectrum equipment, flexibility of spectrum operations, spectrum management, and improvement of policy response capabilities [9]; Strategic Command released in August 2010. Winning the 21st Century Economic and Security Advantage: Strategic Framework for Electromagnetic Spectrum Control, building an electromagnetic spectrum control system architecture from multiple perspectives including objectives, requirements, strategic development, etc. [10]; the Joint Venture Association has promulgated JP6-01 “Joint” in March 2012. “Electromagnetic Spectrum Management Action” joint publication [11], signed in December 2012 CJCSM3320.01C “Chairman’s Handbook of Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Management Operations in Electromagnetic Operation Environment” [12], issued CJCSI3320.01D “Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum” in January 2013 Operational Instructions [13] and CJCSM 3320.04 “Electronic Warfare Supporting Combined Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations” Manual [14]. In March 2015, the “Electromagnetic Spectrum Operational Joint Concept” document [15] was signed, which systematically stated that the Joint Forces launched electromagnetic spectrum combat operations. Strategic vision, organizational structure and functions, command and management relationships, plan formulation and operational implementation, operational integration and action synergy, and gradually Tactical, technical, and program (TTP) refinement of control, interference cancellation, spectrum management, and electronic warfare reprogramming, etc.; US Army released TRADOC P525-7-16, “The US Army’s Future Modular Force Conceptual Capability in December 2007 Plan 2015-2024 – Electromagnetic Spectrum Operation Manual [16]. Field regulations FM6-02.70 “Army Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations” [17] were issued in May 2010. Field Manual FM3-38 “Network Electromagnetic Actions” was issued in January 2014. [18] Published in December 2015, ATP6-02. 70 “Electromagnetic Spectrum Management Combat Operations Skills” [19], updated in February 2016 AR525-15 “Network Reconfiguration of Electromagnetic Action Software” provisions [20], US Air Force updated 2017 AFI10-703 “electronic warfare integrated reprogramming” instructions [21] Define the concept of electromagnetic spectrum operations under the guidance of joint directives, and elaborate on issues such as organization and responsibilities, operational architecture, plan development and coordination control, task list and decision process, action team and management tools, and DOTMLPF, and promote electromagnetics. The integration of spectrum operations, electronic warfare, and cyberspace warfare. In addition, Kevin D, head of the United States Joint Force Development Department. In October 2016, Scott signed the JDN3-16 “Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operation” bulletin[22], standardized terminology and operational framework standards, and made a procedural description of the functional roles, organization, planning, operational implementation, and evaluation. It was awarded the Joint Spectrum Interference Cancellation Program CJCSM3320.02D signed in January and March 2013 by the Joint Committee, CJCSI3320.02F Joint Spectrum Interference Cancellation, and CJCSI3320.02E-1 Joint Spectrum Interference in February 2014. The three major regulations [23][24][25] to eliminate the confidentiality of the program were the important operational support and became the latest guidance for the US military’s electromagnetic spectrum warfare.
1.3 Equipment and Technology
Military technology leads and supports advanced operational concepts. To transform the concept of electromagnetic spectrum warfare from concept to capability, the U.S. military is striving to develop technological innovation and equipment development, and to develop new systems featuring networking, dexterity, multifunction, miniaturization, and adaptability.
On the spectrum management and control system[19][26], the US Department of Defense has developed and deployed the Allied Nations Joint Spectrum Management Planning Tool (CJSMPT) and the Global Electromagnetic Spectrum Information System (GEMSIS) since 2005, followed by the Spectrum XXI and the Modified Spectrum XXIO, Spectrum. Perception Management and Planning System (SSC-SSMPS), Spectrum Situational Sensing System (S2AS), Maritime Electromagnetic Spectrum Operational Action Project (AESOP), Joint Automatic Communication Electronic Action Instruction System (JACS), Host Country Global Online Spectrum Database, etc., with real-time spectrum Measurement and online analysis, spectrum planning and deduction and frequency allocation, electromagnetic interference analysis and conflict elimination, electromagnetic warfare environment modeling simulation, electromagnetic situation sharing and frequency efficiency evaluation, spectrum resource access and database functions and capabilities.
In combat equipment and technology projects [3][26][27], in 2011, the DARPA began to initiate behavioral learning adaptive electronic warfare (BLADE), adaptive radar confrontation (ARC), extreme radio frequency spectrum CommEx, Active Electronic Scan Array (AESA) technology, Near Zero-Power Radio Frequency and Sensor Operation (N-ZERO), under the conditions of the project, through the development of new technologies such as real-time evaluation of countermeasures, autonomous generation of measures, immediate feedback of effects, etc. Unknown waveform and behavioral electromagnetic spectrum threats Real-time tactical confrontation new capabilities; In 2010, the Air Force launched a Cognitive Jammer and HiPERDAC project based on Networked Software Defined Architecture (SDA) and passive RF PRIDE, SWEATER, and CHAMP (Eliminate High-Power Microwave Advanced Missiles) to develop active and passive target threat automatic recognition, real-time assessment and adaptive confrontation technologies and capabilities The US Navy conducts a maritime electronic warfare improvement (SEWIP-Block I/II/III) SLQ-32 shipboard electronic warfare system and ship signalling Equipment (SSEE), electromagnetic command and control (EMC2), integrated mast (InTop) shipborne antenna, next-generation jamming machine (NGJ) and other projects to improve real-time threat assessment and situational awareness, mission program modeling simulation, automatic distribution of electromagnetic spectrum , Combat Operations Analysis and other capabilities; the US Army launched the Electronic Warfare Planning and Management Tool (EWPMT) and Multi-Functional Electronic Warfare (MFEW), Defensive Electronic Assault (DEA) and Silencer Electronics scheduled for September 2016 Warfare and other systems enhance the electronic support for the perception of radio signals and the ability to send electronic signals that interfere with or deceive signals. Earlier this year, the Strategic Command Joint Electronic Warfare Center (JEWC) initiated research on new technologies that provide improved electromagnetic battle management capabilities for electromagnetic spectrum situational awareness and command and control, and plans to implement real-time strategy-based spectrum control and advanced electromagnetic battle sequences (EOB) within five years. ) Characterization and action plan modeling, simulation, analysis, and other capabilities and achieve 7-8 level of technology maturity [28]. Driven by cognitive EW and artificial intelligence technologies, DARPA launched the Radio Frequency Machine Learning System (RFMLS) and Spectrum Joint Challenge Program on August 11, 2017 to develop automatic identification and characterization of target signals from a large number of complex spectrum signals. New technology [29].
2 Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Theory
The electromagnetic spectrum warfare is the latest theory of information warfare of the US military in the 21st century. As research and understanding continue to deepen, the U.S. military will gradually place new strategic ideas as tactics and tactical measures. In order to unify the battlefield electromagnetic spectrum utilization and control actions, the U.S. military issued a series of directives, regulations, regulations, and other documents to publish a summary of the JDN3-16 “Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operation” regulations, and standardized the operational concept, mission category, organization, and combat planning and implementation. Evaluation and so on.
2.1 Basic concepts
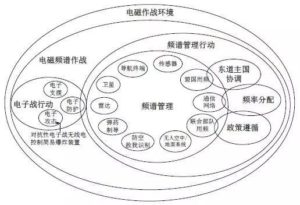
Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations (EMSO) is the conceptual starting point for the US military’s electromagnetic spectrum warfare theory. It is based on electronic warfare and spectrum management and is based on joint electromagnetic spectrum operations. The goal is to achieve electromagnetic spectrum advantages in electromagnetic operating environment (EMOE), involving spectrum management operations, joint electromagnetic spectrum operations (JEMSO) and joint electromagnetic spectrum. Management actions and other concepts. According to the US military regulations JP1-02 “Defense Ministry Military Terms Glossary” [30], JP6-01 “Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Management Action”, JDN3-16 “Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations” and ATP6-02.70 “Electromagnetic Spectrum Management Combat Operations Skills” , United electromagnetic spectrum operations are coordinated military operations carried out by two or more units for use, attacks, protection and management of operational electromagnetic environment. The electromagnetic spectrum management action refers to the interaction between the spectrum management, frequency allocation, host country coordination, policy compliance, and conflict resolution in the entire phase of military operations to jointly promote the planning, management, and implementation of operations within the electromagnetic operations environment. The relationship between various concepts and categories is shown in Figure 1.
Fig. 1 Diagram of related concepts of electromagnetic spectrum operations [19]
2.2 Task Domain Positioning
The U.S. military believes that the joint electromagnetic spectrum combat mission domain is composed of four-dimensional missions of electromagnetic spectrum utilization, management, attack, and protection. Among them, missions include signal intelligence gathering, distribution, and electronic warfare support. Management tasks include electromagnetic spectrum management and electromagnetic battle management. Missions have electronic attacks and navigation warfare, protection tasks have electronic protection and joint spectrum interference cancellation. The operational concept aims to operationally integrate the electromagnetic spectrum operations of the joint forces in the electromagnetic operating environment, establish key priorities, organize action coordination, and eliminate conflicts. Through the full integration of electromagnetic maneuvering schemes, strength and action to strengthen coordination and unification, the electromagnetic spectrum of the battlefield is realized. control. It plays a key role in the formation of joint operational capability in all operational areas, and has a profound impact on the joint forces’ command and control, intelligence, firepower strikes, adjustment and mobility, protection, and maintenance of operational capabilities.
2.3 Organizational Framework
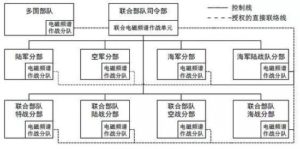
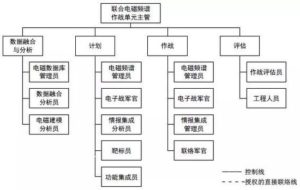
The organization of the joint electromagnetic spectrum operations is responsible for the formulation and publication of policy directives and operational guidelines for commanders and commanders, and for combat planning, operational implementation, coordination of operations, and operational evaluation. The person in charge of electromagnetic spectrum control assigned by the Joint Force Commander shall assume the overall responsibility for the joint electromagnetic spectrum operations. The Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations Unit (JEMSOC) is the chief staff of the Joint Force, and the person in charge of electromagnetic spectrum control assigns a supervisor to direct the command. Each service set up an electromagnetic spectrum operations division, each of which administers an electromagnetic spectrum operational unit, and assumes the functions of integrated network operations, electronic warfare, and spectrum management operations. They are the Army’s electronic warfare officer’s network of electromagnetic action units and the Navy’s maritime operations. The operational center electromagnetic spectrum operational unit, the Air Force air operations center electronic warfare coordination unit, the Marine Corps Combat Development and Integration Command’s cyberspace and electronic warfare coordination unit, and the Multinational Force Joint Staff Operations Department’s contracted electronic warfare coordination unit. The Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operational Organization of the Joint Force is shown in Figure 2. The joint electromagnetic spectrum combat unit architecture is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 2 Electromagnetic Spectrum Operational Organization
Figure 3 Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations Unit Architecture
2.4 Combat Planning Process
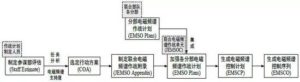
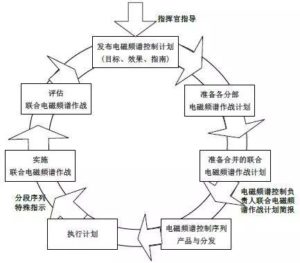
Joint electromagnetic spectrum combat planning is jointly completed by all levels of joint electromagnetic spectrum combat units. During task analysis, the combat plan development team develops a staff assessment plan to determine the electromagnetic spectrum support degree in the formulation and analysis of the action plan as a strategic basis for achieving the advantages of the electromagnetic spectrum; after the action plan is selected, joint electromagnetics are developed. The spectrum operations appendix describes mission tasks, priorities, policy strategies, process steps, and implementation procedures for the entire operational phase, establishing coordination measures, specific procedures, and engagement rules for the use of electromagnetic battle management and control systems in the joint operations domain; The Ministry submits its own electromagnetic spectrum operations plan and integrates it into this appendix. During the planning and implementation of the plan, the Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operations Unit strengthens the electromagnetic spectrum operations plans of each division and participates in the development of various divisions, establishment of priorities, establishment of operational integration and operational coordination, and the creation of an electromagnetic spectrum control plan. Then, the updated electromagnetic spectrum control plan is adjusted to start the joint electromagnetic spectrum combat implementation cycle to generate an electromagnetic spectrum control sequence that guides the use of the electromagnetic spectrum of the joint force. The combat planning process is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Combat Plan Development Process
2.5 Operational methods
The joint electromagnetic spectrum operations implementation process is a continuous cycle of planning, implementation and evaluation. The united electromagnetic spectrum combat unit completes the formulation of the electromagnetic spectrum control plan and the electromagnetic spectrum control sequence, and establishes the combat cycle for combat operations. After the approval of the person in charge of electromagnetic spectrum control, it publishes and organizes the implementation to each branch’s combat unit and unit. The electromagnetic spectrum combat unit fully participates in the key combat flow of the joint force and adjusts the update plan and sequence in time according to the user needs of the subunits and the electromagnetic spectrum of the battlefield during the operation period to ensure that each electromagnetic spectrum control sequence is effectively generated and efficiently Released and executed. The basic processes are: Formulation and release of control plans, update of control plans for each division, preparation of operational plans, generation and distribution of control sequences, execution and adjustment of operational implementation plans and control sequences, and monitoring and guidance of operational processes. The operational implementation cycle is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Joint Electromagnetic Spectrum Operational Implementation Cycle
3 Electromagnetic Spectrum Combat Development Characteristics
New military capabilities cannot be separated from the new system. As an operational concept that responds to new military challenges in the era of information networks, big data, and artificial intelligence, electromagnetic spectrum warfare has become a new direction for the development of the combat effectiveness of the US military. In order to deepen understanding and be efficient and practical, the U.S. military has pushed the new concept to the battlefield from many dimensions, including the development of policy directives, organization and force adjustment, equipment systems and new technology research and development.
3.1 Reinforce basic concepts and theoretical understanding based on policy directives, promote operational concepts and implement operations
Thought leads action. The U.S. military is good at innovative operational concepts and the concept of electromagnetic spectrum warfare is no exception. The first is to focus on clarifying the concept core and uniting the concept. During the early years of the development of the electromagnetic spectrum warfare, new concepts for the new combat domain were always being demonstrated. The military led high-level forums such as the “Old Ravens” and other professional military and military forums to analyze the related theories involved in the concept, exchange technology development and application methods, and promote deeper understanding. At the same time, in the strategic documents and top-level regulations, the relevant old and new policies were gradually sorted out. The links and distinctions between concepts, and the analysis of their categories and task areas, are increasingly contributing to the clear definition of concepts and the formation of theoretical systems. The second is to use operations on the battlefield, and refine the rules step by step. The U.S. military has always attached importance to the concept of combat to the implementation of warfare and technical measures. It took only about three years from the conception of the electromagnetic spectrum to the entry directives and from the joint directive to the arms and military operational manuals and the TTP. The US Army even established a concept blueprint for the use of battlefields before the Joint Staff. Joint operational and operational guidance for systemic operations at the level of the joint level to the unit level.
3.2 Establish an efficient and integrated force structure based on intrinsic power, and strive to use the full cycle of coordination and order in the battlefield
The troops are the carrier of operations. The U.S. military attaches great importance to the optimization and integration of new concept combat forces and existing capabilities. The first is to focus on the overall planning of the capability system. The trajectory of the capabilities of the US military’s electromagnetic spectrum warfare and cyberspace operations is similar. From the Joint Staff Headquarters, the Joint Forces Command to the military arms, set up combat seats and corresponding implementation teams, and establish a full-flow operation mechanism for operational planning, accusation, implementation, and evaluation to form an efficient and smooth capability integration system. The second is to emphasize the coordination and integration of existing institutions and new forces. Through the clarification of the responsibilities and interrelationships of institutions and forces involved in new capabilities in a timely manner, action-oriented operational procedures and implementation procedures are formulated, and even the relevant regulatory templates for coordination activities are promoted to facilitate the whole-system action coordination of electromagnetic spectrum operations and other mission domains. Orderly. The third is relying on actual drills to verify their capabilities in a timely manner. Based on the new concepts of combat and capability goals, the practice of offensive and defensive battles in the field of electromagnetic spectrum is rapidly promoted, and corrections are made during operational trials. The U.S. Army formed an independent electromagnetic spectrum warfare unit of the 1st battlefield network warfare group from February to May last year and plans to participate in an exercise organized by a regional battle commander at the end of the year [31]; the U.S. Air Force is in the “battle shield” exercise. In response to the “Spectrum Interference Elimination Project”, radar EW system evaluation [5] was implemented.
3.3 Promote the pre-research of the new concept equipment system with the support of scientific and technological strength, transform the high technology into the advantage of combat effectiveness
Strong army must have weapon. High-tech equipment is an important way to give birth to newcomer warfare capabilities. The first is to excavate new battlefield changes and assess new demands. The US Department of Defense’s “Electromagnetic Spectrum Strategy” in 2014 pointed out that it is necessary to quantify spectrum requirements and develop the equipment and technologies needed for the electromagnetic environment to enhance real-time spectrum operation and electromagnetic spectrum system real-time identification, prediction and interference cancellation capabilities [9]. From the bottom up to the top, the U.S. military has established a demand collection and integration mechanism for the deployment and deployment of equipment systems and applications. It collects and sorts regularly and conducts special investigations and demonstrations with the aid of the government audit department, Rand Corporation, and a special panel of institutes. The analysis results can be Directly providing decision support for the Ministry of Defense and the Joint Staff Association, it forms an unobstructed demand management evaluation system, and injects activators for the development of electromagnetic spectrum warfare equipment and the development of new combat capabilities. The second is to pay attention to the integration of pre-research technology to equipment system applications. The U.S. military equipment system development will be based on national defense information architecture standards. It will have system processes and capabilities such as simulation modeling, pre-research, technology integration, and application verification. It will focus on the simultaneous improvement of existing models and the development of new research and development of smart technology and equipment systems. “Determining Electromagnetic Waves” pointed out that the important features of the electromagnetic spectrum warfare in the new phase are passive sensor applications and the use of “low-zero-power” capabilities to counteract the enemy’s anti-electromagnetic confrontation, and intelligent technologies and equipment are the future dominant [6]. The pre-research and integration of electromagnetic spectrum warfare technology and equipment will also be able to achieve a more optimal way to upgrade military capabilities to technological capabilities, integrate cutting-edge technologies with mature methods, and integrate specialized systems into integrated platforms, thus achieving a seamless leap in combat effectiveness.
Original Mandarin Chinese:
电磁频谱技术决定未来战争赢家 美军发展现状需警惕
長期以來,為破解反進入/區域拒止(A2 / AD)困局,達成新的抵消戰略,美軍先後推出空地/空海一體戰,網絡中心戰,分佈式殺傷,多域戰和混合戰爭等作戰新思想,不斷謀求導彈攻防,網絡電磁和多域空間等軍事優勢。如今,電磁頻譜戰成為引領新一輪軍事理論和技術創新的新寵。研究和剖析美軍電磁頻譜作戰發展現狀與特點,對於我軍在信息戰場禦敵制勝具有重要現實意義。
1電磁頻譜戰發展現狀
1956年,前蘇聯海軍司令Sergei Gorschkov上將指出:“誰控制了電磁頻譜,誰將贏得下一場戰爭”。六十年後,電磁頻譜成為現代戰爭的關鍵作戰域之一。為爭奪戰場電磁頻譜優勢,美軍從作戰理論到裝備技術進行深入探索,發展迅猛。
1.1理論發展沿革
電磁頻譜控制由來已久。上世紀70年代初,美參聯會主席Thomas H. Moorer稱,第三次世界大戰的勝利者將是能高度控制和管理電磁頻譜的一方。美國“老鴇鴉”協會最早提出將電磁控制(EMC)作為電子戰概念的第四組成部分。2009年,戰略司令部推出電磁頻譜戰(EMSW)早期概念,在電子戰基礎上增加電磁頻譜管理(EMSM),電磁頻譜控制(EMSC),電磁戰鬥控制(EMBC)等任務內容[1]。2012年,戰略司令部建立聯合電磁頻譜控制中心(JEMSCC),旨在實現電子戰和電磁頻譜管理全面集成,各部隊也分別建立相應的組織協調機構和分隊[2]。美海軍同年提出電磁機動戰(EMMW)概念[3],並在2015年3月發布“21世紀海上力量合作戰略”,概要闡述了電磁機動戰目標,構成,技術項目和實現路徑[4]。2015年12月,美國防部首席信息官TerryHalvorsen指出,電磁頻譜有望被視作繼,海,空,天,賽博空間之後第六作戰域[5];同月,戰略與預算評估中心在“決勝電磁波:重拾美國電磁頻譜領域主宰地位”[6]報告中提出“低 – 零功率“電磁頻譜戰概念,闡述了概念思想,趨勢特點,能力和技術需求及當前障礙並提出視圖,概念,採辦,技術,驗證等方面建議。2016年11月底,美國”老鴇鴉“協會第53屆國際研討會以“電磁頻譜作戰全球視野”為主題,展示電子戰,頻譜感知與衝突消除的新概念與技術成果,探討電磁頻譜作戰環境,政策條令,裝備採辦,聯合訓練與作戰能力等[ 7]。2017年1月新任國防部長Ashton Carter簽署首部“電子戰戰略”文件,正式確立電磁頻譜為獨立作戰域並闡述如何實施作戰[8]。
1.2政策與條令
戰略政策與軍事條令集中體現美軍作戰理論發展。美國防部2006年至2014年多版更新“電磁頻譜戰略”,聚焦推進頻譜裝備發展,頻譜行動靈活性,頻譜管理和政策響應能力提升等戰略目標[ 9];戰略司令部2010年8月發布“贏得21世紀經濟與安全優勢:電磁頻譜控制戰略框架”,從目標,需求,戰略開發等多角度構建電磁頻譜控制體系架構[10];參聯會先後於2012年3月頒布JP6-01“聯合電磁頻譜管理行動”聯合出版物[11],2012年12月簽頒CJCSM3320.01C“電磁作戰環境中聯合電磁頻譜管理行動”主席手冊[12], 2013年1月簽發CJCSI3320.01D“聯合電磁頻譜作戰”指示[13]和CJCSM3320.04“電子戰支援聯合電磁頻譜作戰”手冊[14],2015年3月簽署“電磁頻譜作戰聯合概念”文件[ 15,系統闡明聯合部隊開展電磁頻譜作戰行動的戰略願景,組織機構與職能,指揮與管理關係,計劃制定與作實施,作戰集成與行動協同等內容,並逐步向電磁控制,干擾消除,頻譜管理和電子戰重編程等操作層的戰術,技術與程序(TTP)細化;美陸軍於2007年12月發布TRADOC P525-7-16“美陸軍未來模塊化部隊概念能力計劃2015-2024–電磁頻譜作戰”手冊[16],2010年5月頒布野戰條令FM6-02.70“陸軍電磁頻譜作戰”[17],2014年1月頒布野戰手冊FM3-38“網絡電磁行動”[18],2015年12月發布出版物ATP6-02.70“電磁頻譜管理作戰行動技能”[19],2016年2月更新AR525-15“網絡電磁行動軟件重編程“規定[20],美空軍2017年更新AFI10-703”電子戰集成重編程“指示[21],在聯合條令指導下界定電磁頻譜作戰概念範疇,深度闡述機構與職責,作戰架構,計劃制定與協調控制,任務清單與決策流程,行動分隊與管理工具及DOTMLPF等問題,並促進電磁頻譜作戰,電子戰與網絡空間戰的融合。此外,美聯合部隊開發部主管Kevin D. Scott於2016年10月簽署JDN3-16“聯合電磁頻譜作戰”條令紀要[22],規範了術語和作戰框架標準,對職能角色,組織機構,計劃制定,作戰實施和評估作了程序性描述,它以參聯會2013年1月和3月簽頒的CJCSM3320.02D“聯合頻譜干擾消除程序”,CJCSI3320.02F“聯合頻譜干擾消除”和2014年2月的CJCSI3320.02E-1“聯合頻譜干擾消除程序保密增本”三大條令[23] [24] [25]為重要操作支撐,成為美軍電磁頻譜戰最新指導。
1.3裝備與技術
軍事技術引領和支撐先進作戰理念。為將電磁頻譜戰從概念轉化為能力,美軍極力開展技術創新和裝備研發,發展具有網絡化,靈巧化,多功能,小型化和自適應等特徵的新系統。
在頻譜管控系統上[19] [26],美國防部自2005年開發部署同盟國聯合頻譜管理規劃工具(CJSMPT)與全球電磁頻譜信息系統(GEMSIS),隨後的頻譜XXI與改進型頻譜XXIO,頻譜感知管理與規劃系統(SSC-SSMPS),頻譜態勢感知系統(S2AS),海上電磁頻譜作戰行動項目(伊索),聯合自動通信電子行動指令系統(JACS),東道國全球在線頻譜數據庫等,具備實時頻譜測量與在線分析,頻譜籌劃推演與頻率分配,電磁干擾分析與衝突消除,電磁作戰環境建模仿真,電磁態勢共享與用頻效能評估,頻譜資源接入與數據庫等功能與能力。
在作戰裝備與技術項目上[3] [26] [27],2011年,預先研究計劃局(DARPA)開始啟動行為學習自適應電子戰(刀片),自適應雷達對抗(ARC),極端射頻頻譜條件下通信(CommEx),主動電子掃描陣列(AESA)技術,近零功耗射頻和傳感器運行(N-ZERO)等項目,通過對抗行為實時評估,措施自主生成,效果即時反饋等新技術開發針對未知波形和行為的電磁頻譜威脅實時戰術對抗新能力; 2010年,空軍啟動基於網絡化軟件定義架構(SDA)的認知干擾機與大功率高效射頻數模轉換器(HiPERDAC)項目以及無源射頻識別環境(PRIDE),頻譜戰評估技術工程研究(衫),反電子高功率微波先進導彈(CHAMP)等項目,發展有源和無源目標威脅自動感知識別,實時評估和自適應對抗技術與能力;美海軍開展海上電子戰改進(SEWIP-塊1 / II / III)SLQ-32艦載電子戰系統,艦船信號探裝備(SSEE),電磁指揮與控制(EMC2),集成桅杆(InTop)艦載天線,下一代干擾機(NGJ)等項目,提升實時威脅評估與態勢感知,任務方案建模仿真,電磁頻譜自動分配,作戰行動分析等能力;美陸軍啟動計劃在2016年9月投入使用的電子戰規劃與管理工具(EWPMT)和多功能電子戰(MFEW),防禦性電子攻擊(DEA)和“消音器”電子戰等系統,增強射頻信號感知的電子支援和發送干擾或欺騙信號的電子攻擊能力。今年初,戰略司令部聯合電子戰中心(JEWC)啟動面向電磁頻譜態勢感知與指揮控制提供改進電磁戰鬥管理能力的新技術研究,計劃5年內實現基於策略的實時頻譜管控,先進電磁戰鬥序列(EOB)表徵和行動方案建模仿真分析等能力並達到7-8級技術成熟度[28]。在認知電子戰和人工智能技術推動下,DARPA在2017年8月11日又啟動了射頻機器學習系統(RFM LS)和頻譜聯合挑戰項目,開發從大量複雜頻譜信號中自動區分和表徵目標信號的新技術[29]。
2聯合電磁頻譜作戰理論
電磁頻譜戰是美軍21世紀信息作戰最新理論。隨著研究和認識的不斷深化,美軍逐步將新的戰略思想落地為戰法和戰術措施。為統一戰場電磁頻譜利用與控制行動,美軍綜合一系列指示,條令,規程等文件出版JDN3-16“聯合電磁頻譜作戰”條令紀要,規範了作戰概念,任務範疇,組織機構,作戰籌劃與實施及評估等。
2.1基本概念
電磁頻譜作戰(EMSO)是美軍電磁頻譜戰理論的概念基點。它以電子戰和頻譜管理為基礎,以聯合電磁頻譜作戰為實現方式,目標是在電磁作戰環境(EMOE)中達成電磁頻譜優勢,涉及頻譜管理行動,聯合電磁頻譜作戰(JEMSO)和聯合電磁頻譜管理行動等概念。根據美軍條令JP1-02“國防部軍事術語詞典”[30],JP6-01“聯合電磁頻譜管理行動”,JDN3 -16“聯合電磁頻譜作戰”和ATP6-02.70“電磁頻譜管理作戰行動技能”界定,聯合電磁頻譜作戰是由兩個或兩個以上部隊開展的用於利用,攻擊,防護和管理電磁作戰環境的協同軍事行動。電磁頻譜管理行動是指在軍事行動全階段共同促成計劃,管理和實施電磁作戰環境內作戰行動的頻譜管理,頻率分配,東道國協調,政策遵循,衝突消除等相互聯繫的功能。各概念間關係與範疇如圖1。
圖1電磁頻譜作戰相關概念關係圖[19]圖1電磁頻譜作戰相關概念關係圖[19]
2.2任務域定位
美軍認為,聯合電磁頻譜作戰任務域由電磁頻譜利用,管理,攻擊和防護四維度任務構成,其中,利用任務有信號情報蒐集分發和電子戰支援,管理任務有電磁頻譜管理和電磁戰鬥管理,攻擊任務有電子攻擊和導航戰,防護任務有電子防護和聯合頻譜干擾消除。該作戰概念旨在對電磁作戰環境中的聯合部隊電磁頻譜行動進行作戰集成,確立重點優先事項,組織行動協同和衝突消除,通過充分集成電磁機動方案,力量和行動強化協調統一,實現戰場電磁頻譜控制。它在各作戰域的聯合作戰行動能力形成中扮演著關鍵角色,對聯合部隊的指揮控制,情報,火力打擊,調整與機動,防護,行動能力維持等職能作用發揮產生深刻影響。
2.3組織機構框架
聯合電磁頻譜作戰的組織機構負責為指揮官和司令部制定和發布政策指示與行動指南,進行作戰計劃制定,作戰實施,行動協調和作戰評估。由聯合部隊指揮官指派電磁頻譜控制負責人承擔聯合電磁頻譜作戰總職責。聯合電磁頻譜作戰單元(JEMSOC)是聯合部隊的主要參謀部,由電磁頻譜控制負責人委派一名主管統一指揮。各軍種設立電磁頻譜作戰分部,各下轄一個電磁頻譜作戰分隊,承擔集成網電作戰,電子戰和頻譜管理行動的職能,分別為陸軍的電子戰軍官所轄網絡電磁行動分隊,海軍的海上作戰中心電磁頻譜作戰分隊,空軍的空中作戰中心電子戰協調單元,海軍陸戰隊的戰鬥開發與集成司令部下屬網絡空間與電子戰協調單元,多國部隊聯合參謀部作戰處所屬合同電子戰協調單元。聯合部隊所屬聯合電磁頻譜作戰組織機構如圖2,聯合電磁頻譜作戰單元架構如圖3。
圖2電磁頻譜作戰組織機構圖2電磁頻譜作戰組織機構
圖3聯合電磁頻譜作戰單元架構圖3聯合電磁頻譜作戰單元架構
2.4作戰籌劃流程
聯合電磁頻譜作戰籌劃工作由各級聯合電磁頻譜作戰單元共同完成。在任務分析時,作戰計劃制定隊伍制定一份參謀部評估方案,用於在制定和分析行動方案中確定電磁頻譜支持度,作為達成電磁頻譜優勢的戰略基礎;行動方案選定後,制定聯合電磁頻譜作戰附錄,描述作戰全階段的使命任務,優先事項,政策策略,流程步驟和實施程序,為在聯合作戰域使用電磁戰鬥管控系統建立協調措施,具體程序和交戰規則;同時,聯合部隊各分部報送各自電磁頻譜作戰計劃並集成到該附錄在計劃制定與行動實施期間,聯合電磁頻譜作戰單元加強各分部電磁頻譜作戰計劃並參與各分部需求制定,優先事項確立,作戰集成與行動協同,並生成一份電磁頻譜控制計劃。隨後,調整更新後的電磁頻譜控制計劃啟動聯合電磁頻譜作戰實施週期環,生成指導聯合部隊磁頻譜使用的電磁頻譜控制序列。作戰籌劃流程如圖4。
圖4聯合電磁頻譜作戰計劃制定流程圖4聯合電磁頻譜作戰計劃制定
2.5作戰實施方式
聯合電磁頻譜作戰實施過程是一個計劃,實施和評估的連續循環週期。聯合電磁頻譜作戰單元完成電磁頻譜控制計劃和電磁頻譜控制序列的制定,確立作戰行動的戰鬥週期,經電磁頻譜控制負責人批准,向各分部作戰單元和分隊發布並組織實施。電磁頻譜作戰單元全週期完整參與聯合部隊關鍵戰鬥流程,並根據作戰時段內各分部所屬分隊的用戶需求和戰場電磁頻譜態勢及時調整更新計劃與序列,確保每份電磁頻譜控制序列有效生成,高效下達和執行基本過程為:制定與發布控制計劃,更新各分部控制計劃,準備作戰計劃,生成和分發控制序列,執行和調整作戰實施計劃與控制序列,監測和指導作戰進程,作戰實施週期如圖5。
圖5聯合電磁頻譜作戰實施週期圖5聯合電磁頻譜作戰實施週期
3電磁頻譜作戰發展特點
軍事新能力離不開新體系支撐。作為應對信息網絡,大數據和人工智能時代軍事新挑戰的作戰理念,電磁頻譜戰一經提出就成為美軍戰鬥力發展新方向。為力求深化認識且高效實用,美軍從政策條令建設,組織機構與部隊調整,裝備系統與新技術研發等多個維度將新概念推向戰場。
3.1以政策條令為依據強化基本概念與理論認知,推動作戰理念向執行操作落地
思想引領行動。美軍擅長創新作戰理念,電磁頻譜戰概念也不例外。一是注重釐清概念核心,統一理念認知。電磁頻譜戰發展的早期數年,始終在論證面向新作戰域的新概念。軍方主導“老鴇鴉”等專業性軍地高層論壇,分析概念所涉及的相關理論,交流技術發展和應用方式,推動認識深化,同時,在戰略性文件和頂層條令中,逐步梳理相關聯新舊概念間的聯繫與區別,剖析其範疇與任務域,以此日益促成概念的清晰界定和理論體系成型。二是面向戰場運用操作,逐層細化條令。美軍歷來重視將作戰概念向執行層戰,技術措施細化落地。電磁頻譜戰從概念提出到進入條令和從聯合條令到軍兵種配套行動手冊及戰技術規程(TTP)僅用三年左右的時間,美陸軍甚至在聯合參謀部之前建立戰場運用概念藍圖,形成從聯合層面到分隊層面層層銜接,逐項落的系統性作戰運用與操作指南。
3.2以固有力量為基礎建立高效集成的部隊架構,力求戰場運用全週期協調有序
部隊是行動載體。美軍非常重視新概念作戰力量與現有能力的優化集成。一是注重能力體系整體規劃。美軍電磁頻譜戰與網絡空間作戰的能力發展軌跡相似。從聯合參謀部,聯合部隊司令部到軍兵種部隊,設置作戰席位和相應實施分隊,建立作戰計劃,指控,實施和評估的全流程運行機制,形成高效流暢的能力集成體系。二是重視現有機構與新力量協調互融。通過及時明確新能力所涉及機構與力量的職責和相互關係,制定面向作戰的行動流程和實施程序,甚至規定有關協調活動中的制式模板,促成電磁頻譜作戰與其他任務域的全體系全程行動協同有序。三是依托實戰演練及時驗證能力。基於作戰新概念和能力目標迅速推進電磁頻譜領域戰場攻防研練實踐,在作戰試驗中邊驗證邊修正。美陸軍在去年2至5月成立第1戰場網電戰小組的電磁頻譜戰獨立分並計劃年底參加某一地域戰鬥司令部組織的演習[31];美空軍在“戰鬥護盾”演習中為響應“頻譜干擾消除項目”實施了雷達電子戰系統測評[5]。
3.3以科技實力為支撐推進新概念裝備系統預研,將高新技術向戰鬥力優勢轉化
強軍必需利器。高新技術裝備是催生新生作戰能力的重要途徑。一是善於發掘戰場新變化並評估新需求。美國防部2014年“電磁頻譜戰略”指出,要量化頻譜需求,發展電磁環境所需裝備和技術,增強實時頻譜操作和電磁頻譜系統實時識別,預測及干擾消除等能力[9]。美軍由底至頂建立了面向裝備系統研建與作戰部署應用的需求採集與集成機構,在定期蒐集梳理的同時借助政府審計署,蘭德公司和院所專題小組進行專項調研論證,分析結果可直接為國防部和參聯會提供決策支持,形成了暢通有力的需求管理評估體系,為研建電磁頻譜戰裝備和開發新型戰鬥力注入激活劑。二是注重預研技術向裝備系統集成應用。美軍裝備系統研建都會基於國防信息體系結構標準展開,具備仿真建模,預先研究,技術集成,應用驗證等系統流程和完善能力,注重同步進行原有型號改進和新研智能技術裝備系統開發“決勝電磁波”指出,新階段電磁頻譜戰重要特徵是無源傳感器應用和採用“低 – 零功率”。能力對敵進行反電磁對抗,智能化技術和裝備是未來主導[6]。電磁頻譜戰技術裝備預研與集成也將能夠以更優方式實現軍事問題向技術能力升級,前沿技術與成熟方法互融,專用系統向綜合平台集成,進而完成戰鬥力優勢無縫躍升。
Original Source:
http://mil.news.sina.com.cn/jssd/2018-05-03/