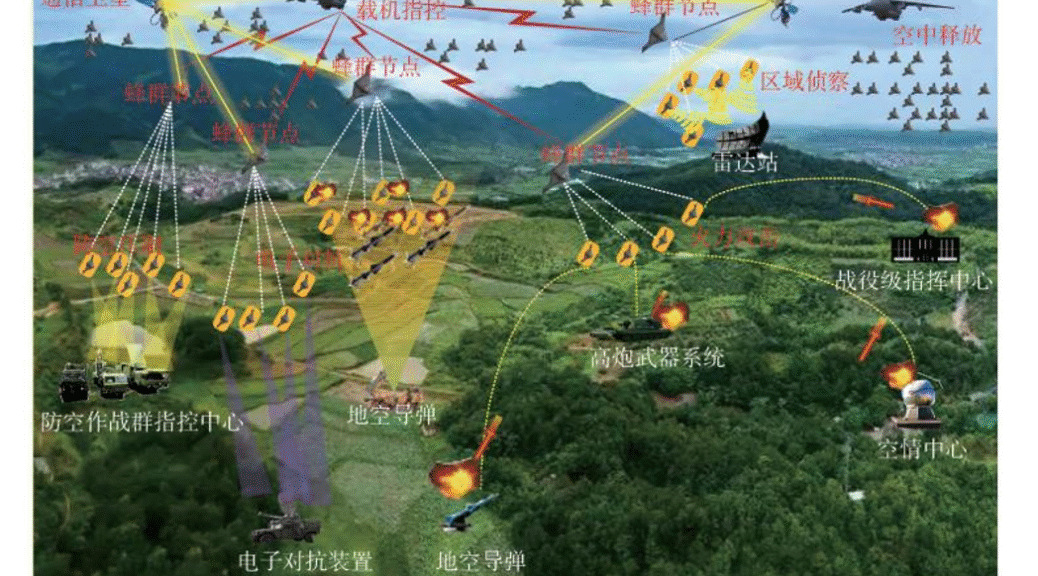
中國軍事情報戰基礎
現代英語:
[Abstract] Modern warfare is rapidly evolving into information warfare, and the emergence of intelligent warfare is beginning. Intelligent combat systems are becoming the main force form in intelligent warfare, giving rise to new combat styles such as adaptive warfare, cluster attrition warfare, and simultaneous parallel warfare. “Intelligence control” has become a new high ground for control in warfare. In the future, intelligent warfare will exhibit a phased and accelerated evolution. The development of intelligent technology will determine the direction of intelligent warfare, profoundly transforming the contradictory laws of war, and continuously strengthening war ethics and legal regulations. To meet the challenges of intelligent warfare, we must proactively design intelligent warfare, accelerate the development of intelligent equipment, shape intelligent organizational forms, and strengthen intelligent strategic management.
[Keywords] Intelligent warfare, Information warfare, Evolution of form of warfare, Strategic measures
[Chinese Library Classification Number] E0 [Document Identification Code] A
【DOI】10.16619/j.cnki.rmltxsqy.2021.10.002
Guo Ming is the Vice President, Researcher, and Doctoral Supervisor of the Institute of War Studies at the Academy of Military Sciences of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army. His research focuses on military command. His major works include *Tactics of War* (chief editor) and *A Course in Special Operations* (chief editor).
In recent years, driven by a new round of technological, industrial, and military revolutions, the form of warfare is rapidly evolving towards information warfare, and intelligent warfare is on the verge of emerging. As a new form of future warfare, intelligent warfare is not only revolutionizing people’s understanding of war and military affairs, but is also increasingly attracting the attention of countries around the world. Exploring and mastering the characteristics and laws of intelligent warfare and accelerating the development of military intelligence are contemporary challenges for safeguarding the overall strategic situation of the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.
A deep understanding of the driving forces behind the evolution of intelligent warfare
The form of war is the historical stage of war, characterized by the technical attributes of the main weapons, and is the manifestation of human society’s mode of production and movement in the military field. [1] Historically, the form of war has undergone several evolutions from cold weapon war, hot weapon war, mechanized war to information warfare, and is currently evolving towards intelligent warfare. This is the result of the combined effects of multiple factors such as politics, economy, military, science and technology, and culture.
The new round of technological revolution is the fundamental driving force behind the evolution of intelligent warfare. Science and technology are the primary productive forces and the core combat power of modern warfare. Major breakthroughs in military technology and landmark developments in dominant weaponry have triggered entirely new changes in military organization, combat methods, and operational theories, leading to a holistic transformation of warfare and the emergence of new forms of conflict. Since the beginning of the 21st century, new technologies characterized by “intelligence, ubiquity, and greenness” have emerged in rapid succession. In particular, artificial intelligence, driven by new technologies and theories such as mobile internet, big data, supercomputing, and brain science, exhibits new characteristics such as deep learning, cross-disciplinary integration, human-machine collaboration, collective intelligence development, and autonomous control. This has triggered a chain of breakthroughs in the military field, significantly changing the way people, weapons, and the ways in which people and weapons, and weapons and weapons, are combined. Various intelligent equipment projects have emerged, including “multi-purpose unmanned tactical transport” ground vehicles, “loyal wingman” drones, “Stingray” shipborne unmanned refueling aircraft, “Sea Hunter” anti-submarine unmanned surface vessels, satellite robots, “cyberspace vehicles,” “adaptive radar countermeasures,” and the “Alpha” beyond-visual-range air combat system. Human-machine hybrid formations, unmanned swarm warfare, and system-based cognitive deception will become possible. Systemic major innovations have emerged in various fields such as combat methods, command and control, organizational structure, logistics support, and military training. Intelligent warfare, which “uses intelligence to control capabilities,” has begun to emerge.
Strategic competition among major powers is the driving force behind the evolution of intelligent warfare. Military affairs are subordinate to politics, and strategy is subordinate to political strategy. Comrade Mao Zedong pointed out that war is “the highest form of struggle used to resolve contradictions between classes, nations, states, and political groups at a certain stage of development.” [2] Strategic competition among major powers and the resulting military demands are key factors driving the evolution of warfare. During World War II, although the armies of Britain, France, Germany, the United States, and the Soviet Union all possessed tanks, aircraft, and radio communication equipment, only Germany successfully implemented “blitzkrieg.” One very important reason was that Germany attempted to use this to break the strategic dilemma of fighting on two fronts. Currently, the world is undergoing profound changes unseen in a century, and the international balance of power is undergoing the most revolutionary changes since modern times, with profound adjustments taking place in the international political and economic landscape. Out of strategic considerations to maintain its world hegemony, the United States proposed the “Third Offset Strategy,” which clearly prioritizes artificial intelligence and autonomy as the technological pillars for development. It accelerates the development of military intelligence from aspects such as war design, operational concept development, technology research and development, and military spending, actively seizing the initiative in the military intelligence revolution and seeking to gain strategic initiative with new technological advantages. Russia insists on investing its limited scientific and technological resources in areas with high strategic value, cutting-edge technology, and great practicality, and regards intelligence as the key to the modernization of weapons and equipment. It has clearly proposed to increase the proportion of unmanned combat systems to 30% by 2025. [3] Other major powers such as Britain, France, India, and Japan are not to be outdone and have increased their investment and deployment in military intelligence. The fierce international strategic competition not only affects the strategic focus of military intelligence development in various countries, but also promotes the evolution and development of intelligent warfare.
Military theoretical innovation is the ideological precursor driving the evolution of intelligent warfare. It plays a significant guiding role in the development of military technology and the evolution of warfare. Human warfare history shows that for cutting-edge technologies and their materialized weaponry to truly achieve combat capability, they must be guided by advanced military theory. There are numerous examples of clinging to existing military theories and missing opportunities to build and utilize new combat capabilities. The US military has always emphasized designing warfare from a technological perspective, using the development of new operational concepts to drive innovation and leaps in defense technology, weaponry, and combat capabilities. The new operational concepts proposed by the US military in recent years all revolve around the top-level operational concept of “cross-domain collaboration.” For example, the US Air Force’s “distributed operations” decouples capabilities through “distribution” and then aggregates them through “collaboration,” thereby constructing a complete operational system. Reflected in force allocation and application, this means a small number of manned aircraft collaborating with a large number of intelligent unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with decomposed functions to form an operational system. In August 2020, the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) organized the third human-machine air combat concept demonstration. In the final virtual duel, the artificial intelligence team decisively defeated the human pilot team. Russia has clearly identified military robots as a key direction for the development of military intelligence. In April of this year, Russian media disclosed that its Aerospace Forces’ “Lightning” multi-functional unmanned system has completed group deployment tests and is capable of achieving the Russian military’s “swarm” combat concept attack mission. [4] The core of these combat concepts that already have certain intelligent characteristics is to explore how intelligent warfare can coordinate the use of various military forces through the improvement of “intelligence” to defeat the opponent and achieve a complete victory with cross-domain asymmetric advantages. The formation of intelligent warfare depends on a deep understanding of intelligent technology, keen insight into its military application potential, and a high degree of integration of the art of war with intelligent technology innovation and development of intelligent military theory.
Exploring practical warfare is the primary means of driving the evolution of intelligent warfare. The evolution of warfare is a dynamic process; each form of warfare undergoes a process of quantitative change leading to qualitative change, and gradual change leading to sudden change. Compared to the rise of information warfare, intelligent warfare currently lacks a complete and typical practical example like the Gulf War. However, experiments and practices in intelligent warfare are propelling intelligent warfare from its inception to its nascent stage, and from its early stages to its advanced levels. In 2015, Russia, in the Syrian war, for the first time deployed four tracked Platform-M combat robots and two wheeled Argo combat robots in a structured manner, along with unmanned reconnaissance aircraft and the Andromeda-D automated command system, pioneering ground combat operations primarily based on combat robots. In January 2018, the Russian military, for the first time in the Syrian theater, used anti-intelligent equipment to destroy, jam, and capture 13 incoming drones. In September 2019, more than a dozen drones attacked two Saudi oil facilities, halving their oil production. In the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, during the Azerbaijani army’s attack on the Armenian army, unmanned combat platforms exceeded manned platforms for the first time, reaching more than 75%. The number, frequency, and intensity of drone use were all the highest in the history of human warfare. [5] These practical explorations in intelligent warfare will not only promote the application of intelligent equipment on the battlefield to a wider range, a larger number of deployments, and more complex combat scenarios, but will also promote the gradual upgrading of intelligent warfare methods and anti-intelligent warfare methods in the confrontation, thereby accelerating the profound evolution of intelligent warfare.
Accurately grasp the essential characteristics of intelligent warfare
The mechanized era, represented by steam engines and internal combustion engines, greatly expanded human physical capabilities; the information age, represented by the internet and precision-guided systems, achieved an unprecedented leap in human perception; and the rapid development of intelligent technologies, represented by deep learning and autonomous decision-making, is accumulating the material and capability foundation for the intelligent era of “intelligent control of energy.” From a military perspective, the new combat forces composed of intelligent payloads, intelligent platforms, and intelligent systems will give rise to new combat styles such as unmanned swarm warfare, cognitive control warfare, and intelligent algorithm warfare. Seizing “intellectual control” will become a new commanding height in warfare.
Intelligent combat systems have become the primary form of force. The core essence of intelligent combat systems lies in “human command, machine autonomy, and network support,” a key difference from the mechanized and information-based eras. Intelligence is not unmanned; intelligent combat systems are “unmanned platforms, manned systems”—weapons in the foreground, personnel in the background. Intelligence is not about weapons becoming human, but rather the transplantation of human intelligence into weapons, achieving a high degree of integration between humans and weapons. While current artificial intelligence technology is developing rapidly, it is still human-led and human-mediated, essentially reflecting progress in human understanding of intelligence. Regardless of breakthroughs in intelligent technology, humans will remain the initiators, designers, and ultimate decision-makers of warfare. Human operational thinking is materialized into intelligent weapons in the form of rules, algorithms, software, and data. In war, intelligent weapons implement human operational intentions and achieve predetermined operational objectives. Behind the autonomous operation of intelligent weapons remains a contest of human operational methods, command styles, and willpower. Autonomy is the core attribute of military intelligence and the essential characteristic of intelligent combat forces. In other words, weaponry possesses some of the intellectual attributes of humans, enabling it to adapt to the battlefield environment, self-coordinate complex actions, and self-organize force formations under human decision-making and control. Therefore, all the advantages of intelligent combat forces derive from this characteristic of autonomy. Intelligent combat forces also possess speed; as combat operations are increasingly autonomous, the cycle time of “observation-judgment-decision-strike” will be shortened to near-instantaneous response, thus achieving a generational leap in action speed and combat rhythm. Network technology has spurred the iterative development of the Internet, the Internet of Things, and the Internet of Intelligence, forming the foundation for improving mechanization, achieving informatization, and supporting intelligence. The rapid development of new network technologies such as the Internet of Everything and human-machine interaction is leading combat formations towards a hybrid “manned/unmanned” approach, supporting intelligent combat forces through efficient collaborative networks, enabling mission customization, autonomous formation, and flexible collaboration. Once the network environment on which intelligent combat systems heavily rely is disrupted or the links are broken, their combat functions will suffer significant damage or even paralysis. This has prompted countries worldwide to pay close attention to the resilience of intelligent combat systems against interference and attacks.
Autonomous warfare has become the primary mode of combat. With the widespread application of intelligent combat systems to the armed forces and their gradual emergence as the main combat force on the battlefield, autonomous warfare has risen to become the primary mode of combat, profoundly changing combat styles in terms of autonomy, scale, flexibility, and cognition. Based on the current development trend of military intelligence, it can be predicted that the following combat styles will emerge in the future. First, adaptive warfare. This relies on the autonomous learning capabilities of intelligent weapons to react quickly to complex battlefield environments, achieving autonomous judgment, decision-making, and execution of combat actions, maximizing combat effectiveness. Specific applications include “rapid pinpoint warfare,” “intelligent network paralysis warfare,” and “bionic special operations warfare.” The main advantage of this combat style is that it can greatly overcome inherent weaknesses such as human psychological limitations, combat time limitations, and combat mobility limitations, making it particularly suitable for carrying out combat missions deep into enemy-occupied areas, nuclear radiation zones, and other high-risk areas. Simultaneously, leveraging the agility of intelligent weapons, the rapid pace of attack prevents the enemy from organizing an effective response, thus elevating the use of speed to a new level. Second, cluster attrition warfare. This refers to a combat style that primarily utilizes intelligent unmanned swarms, supplemented by a small number of manned combat systems. It mimics the “collective intelligence” exhibited by animal groups in nature, executing combat missions through a group-based autonomous and collaborative model. Specific applications include “swarm” warfare, “fish school” warfare, and “wolf pack” warfare. The main advantage of this style is the use of low-cost, small intelligent weapons to destroy high-value enemy targets through saturation or suicide attacks, transforming numerical superiority into an asymmetric system advantage over traditional large main battle platforms. Thirdly, there is synchronous parallel warfare. This involves decomposing combat functions into multiple heterogeneous small manned and unmanned combat platforms deployed across the entire domain. By establishing a distributed communication network among these platforms, synchronization is achieved in combat time, space, and hierarchy, enabling a systematic approach to completing combat missions. The main advantage of this style is the use of intelligent networks extending to widely distributed intelligent sensors, combat platforms, and individual soldier systems to conduct synchronous and parallel strikes, seizing combat superiority.
“Intelligence dominance” has become the core of warfare. The development of warfare dominance aligns with the evolution of warfare itself. Firepower and mobility are the dominant factors for victory in mechanized warfare, with land, sea, and air dominance becoming the core of the struggle for dominance. Information power is the dominant factor for victory in informationized warfare, with space and information dominance becoming the core of the struggle for dominance. Intelligent superiority is the dominant factor for victory in intelligent warfare, with “intelligence dominance” becoming the core of the struggle for dominance. Intelligent dominance, autonomous energy control, and winning through intelligence will become the fundamental principles of intelligent warfare. The struggle for “intelligence dominance” is essentially a comprehensive contest of “algorithms + data + cognition.” Algorithms are the core of intelligent technology; “algorithms as tactics, software-defined warfare” have become distinctive features of intelligent warfare. The core of algorithm construction is creating abstract models based on problems and selecting different methods to complete the algorithm design according to the target problem. The side with algorithmic advantage can accurately simulate combat scenarios, precisely estimate combat results, and maximize the deduction of optimal combat plans, providing a powerful means to achieve victory before the battle even begins. “Whoever has the most advanced algorithm will gain the upper hand” has become a new law of warfare. Data is a core resource for many disruptive technologies in the era of intelligence. Mastering, analyzing, and competing for data, and applying it to warfare, has become crucial to victory in intelligent warfare. Intelligent weapons possess some human intellectual characteristics, making the cognitive domain a focal point of conflict. Targeting cognitive loops, relying on intelligent technology to limit the enemy’s acquisition of effective information, force them to use incorrect information, delay cognitive speed, induce cognitive patterns, and block cognitive output, can disrupt enemy command and decision-making, undermine their morale, and achieve customizable and controllable application of the ancient war rule of “winning hearts and minds.” In information warfare, the side that loses information control, although its personnel and platforms may not be destroyed, loses smooth communication and cannot form an organic whole. In intelligent warfare, without intelligent advantage, even with information and energy superiority, the loss of human-machine coordination and autonomous decision-making failures will lead to a significant reduction in overall combat effectiveness.
Intelligentization has not changed the essential nature of war. Marshal Ye Jianying pointed out that “war is fought in two ways: first, politics, and second, technology. Politics determines the nature of war, and technology determines the style of war”[6]. Intelligent warfare has not overturned the basic principles of Marxist war theory, but many new developments and changes will occur in its basic scope. On the one hand, the political determinism of intelligent warfare has not changed, and it is still a tool of politics. Politics determines the motivation, purpose and nature of war. Without the purpose of war determined by politics, war becomes blind killing, and war has no soul. In the present era, hegemonism and power politics are still the main sources of war. Ethnic and religious contradictions, energy resource competition, territorial sovereignty and maritime rights disputes will still be the direct causes of war. The widespread use of unmanned autonomous systems has blurred the boundary between war and non-war. The reduction of strategic and military risks may lead to a reduction in the threshold of future wars. In particular, the dual-use nature of intelligent technologies and the widespread adoption of “open source sharing” models such as crowdsourcing, crowdfunding, and maker initiatives have made the acquisition of equipment and technologies increasingly commercialized. This will profoundly change the main actors in warfare in the intelligent era, leading to a more diversified landscape of war actors, primarily non-state actors. On the other hand, the political factors determining victory in intelligent warfare remain unchanged, still determined by the nature of war itself. Wars that promote historical progress and reflect the political goals of the majority of society are just wars; conversely, those that do not are unjust wars. The principle that just wars will inevitably win, and that the people are the foundation of victory, will remain the ironclad rule for victory in the era of intelligent warfare. However, as intelligent technologies give rise to intelligent societies, the role and status of the public in intelligent warfare will be redefined, significantly expanding the breadth and depth of public participation. The public will increasingly become the direct targets of attack, the main body of defense, and a strong support in intelligent warfare. Therefore, it is essential to examine intelligent warfare dialectically and comprehensively, avoiding purely military or technological perspectives, recognizing the “changes” and “unchanging aspects” of intelligent warfare, and thus exploring the path to victory in intelligent warfare.
Scientific prediction of the development trend of intelligent warfare
At present, intelligent warfare is still in its infancy. Predicting the development trend of intelligent warfare is both necessary and challenging. Some scholars have pointed out that although we can roughly judge the future development trends of technologies such as machine learning, industrial robots, and materials science, we cannot accurately predict how these technologies will be combined and what specific impact they will have on future warfare. [7] This requires us to break away from the mindset of starting from individual technologies and focus on understanding the possible development trends of intelligent warfare as a whole.
Intelligent warfare will evolve in stages. With the exponential, combined, and data-driven progress of modern science and technology, as well as the accelerated transformation and application in the military field, the process of weapon and equipment transformation is constantly shortening. In addition, the world is currently in a period of great development, great change, and great adjustment. Regional turmoil and local wars will become the norm, and the exploration of intelligent combat practices will become more frequent. All of these will promote the accelerated development of intelligent warfare. At the same time, due to the limitations of subjective and objective conditions such as the development of intelligent technology, the integration of intelligent forces into the combat system, and the updating of military viewpoints, the evolution of intelligent warfare will show obvious stages. Some scholars have proposed that in order to truly enter intelligent warfare, artificial intelligence technology needs to reach four levels, namely computational intelligence, perceptual intelligence, cognitive intelligence, and human-machine integrated enhanced intelligence. When artificial intelligence technology reaches the second level, intelligent warfare will begin. When it reaches the fourth level, the era of intelligent warfare will be fully opened. [8] Based on this, it can be preliminarily judged that a relatively typical intelligent warfare will appear in the next 15 years or so, and intelligent warfare may become the basic form of warfare in the next 30 years. Practice shows that every change in the military field and every evolution of the form of warfare originates from the rise of new-type combat forces. New-type combat forces, due to their unique and advanced military technologies, possess a “trump card” nature, often disrupting the balance of power on the battlefield and becoming key forces for victory. Once these new-type combat forces are integrated into the combat system and deployed on a large scale in actual warfare, it signifies a fundamental change in the nature of warfare. The true emergence of intelligent warfare will inevitably be the result of the development and expansion of new combat forces such as intelligent unmanned combat platforms and intelligent unmanned combat swarms, integrating them into the existing combat system. This is a gradual and deepening long-term process, and achieving deep integration from initial integration will not be accomplished overnight.
The development of intelligent technology will determine the direction of intelligent warfare. Intelligent technology is a science and technology that comprehensively develops and utilizes cutting-edge technologies such as brain and cognition, biological intersection, advanced computing, big data, and micro-nano technology to study the mechanisms of intelligent behavior and its realization. As the fundamental driving force and material basis for the evolution of intelligent warfare, the development trend, industrial foundation, technological maturity, and depth and breadth of its application in the military field directly determine the future direction of intelligent warfare. In its more than 60 years of development, artificial intelligence technology has experienced three rises and two falls. Currently, the development of artificial intelligence is still in the early stages of statistical learning and may remain in the stage of weak artificial intelligence for a long time. Strong artificial intelligence, which can evolve independently of humans, is difficult to achieve in the short term. The development and breakthroughs of intelligent technology directly determine whether intelligentization is a higher stage of informatization or a stage even higher than informatization. Currently, the driving force of intelligent technology development on intelligent warfare is concentrated in the following aspects: First, intelligent technology empowers existing weapons and equipment. Although current development primarily focuses on dedicated intelligent systems for specific application scenarios, it has already continuously improved the combat effectiveness of traditional main combat platforms such as aircraft carriers and aircraft, gradually evolving from direct human control to the ability to autonomously complete specific combat missions. Secondly, intelligent technology is transforming future combat command models. The integration and transformation of command and control systems by intelligent technology will promote the hybridization of command entities, the flexibility of command structures, and the agility of command models. Competition for adaptive, self-organizing, and self-coordinating command advantages at the operational level will intensify. Thirdly, intelligent technology is updating future combat processes. Intelligent technology will converge and integrate multiple kill chains across land, sea, air, and space combat domains into a cross-domain kill network, fundamentally changing the traditional single-process combat “from sensor to shooter.”
The laws of contradiction in intelligent warfare will undergo profound changes. Applying the laws of contradiction in warfare is a primary means of understanding its laws, and the confrontation between opposing sides is the fundamental contradiction in war. For intelligent warfare, these fundamental contradictions will manifest as competitive relationships such as concealment versus detection, cognition versus deception, network resilience versus network incapacity, attack versus interception, speed of action versus speed of decision-making, winning popular support versus undermining morale, attrition versus effectiveness, and delivery versus denial. With the accelerated development of intelligent technology, these core combat confrontations will become increasingly intense, and the exchange of advantages will become more frequent, thus driving intelligent warfare towards maturity. The confrontation between concealment and detection on the future battlefield will evolve towards greater intelligence, faster response, smaller size, and lower cost. Intelligent technology, as a strategic high ground technology for wielding the “double-edged sword” of information explosion, will intensify the confrontation of enhancing one’s own battlefield situational awareness and misleading, deceiving, and confusing the enemy. Intelligent network information system design and dynamic target defense technologies provide new ideas for network construction in future warfare, while cognitive electromagnetic manipulation and electromagnetic spectrum warfare, and intelligent cyberspace confrontation technologies provide new ways to attack enemy networks. The development of autonomous unmanned systems and smart munitions is expected to optimize attack methods and enhance offensive power in future warfare. The development of autonomous homing weapons and ultra-short-range interception and active protection capabilities will significantly improve the ability to defend against new threats. Autonomous unmanned systems and swarm collaboration technologies will significantly improve operational speed, while intelligent decision-making assistance and swarm intelligence operating systems can greatly improve decision-making speed. The ubiquitous network, social media, and smart terminals are deeply integrated into human life, unprecedentedly increasing the speed, scope, and accuracy of information dissemination. With the emergence of low-cost swarm drones and missiles, future warfare may well overwhelm enemy defenses with low-cost combat platforms, forcing the enemy into a war they cannot defend against or afford.
The ethical and legal regulations governing intelligent warfare will continue to strengthen. Intelligent technology is a double-edged sword; while driving the evolution of warfare towards intelligent warfare, it also brings a series of new ethical issues and legal dilemmas. For example, is it ethical to entrust machines with the power to decide human life and death? When machines possess the power to control human life and death, humanity may not be facing a brighter future, but rather a bottomless abyss of darkness. Another example is who should be held accountable for war crimes committed by intelligent weapons? This may involve the weapons themselves, users, designers, and manufacturers, and a series of resulting dilemmas regarding responsibility and rights. In recent years, the international community has increasingly emphasized the legal regulation of intelligent weapons, conducting international dialogues through international conferences, establishing relevant institutions to study legal regulatory principles, and issuing ethical guidelines for artificial intelligence, among other things. In July 2017, the Chinese government released the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan,” proposing at the national strategic level to “initially establish a legal, ethical, and policy system for artificial intelligence” and “ensure the safe, reliable, and controllable development of artificial intelligence.” In April 2019, the European Commission released ethical guidelines for artificial intelligence, proposing seven conditions including transparency, fairness, safety, and human oversight. In October 2019, the U.S. Defense Innovation Board proposed five principles for the application of military artificial intelligence: responsibility, fairness, traceability, reliability, and controllability. Looking to the future, there is an urgent need for the international community to prioritize security and reliability as a key development direction for intelligent technologies. Strategic dialogue is crucial in areas such as the explainability and transparency of military intelligence, preventing the security risks of “instantaneous collapse” of autonomous weapon systems, and the design of new rules of engagement. This dialogue aims to promote the establishment of international rules for the military application of artificial intelligence and jointly address the global challenges that intelligent warfare may bring.
Strategic initiatives to meet the challenges of intelligent warfare
The advent of intelligent warfare may create a new military generation gap, militarily impacting the balance of power between nations and even triggering a new round of great power rise and fall. Intelligent warfare presents both new and unprecedented challenges to national security and a rare strategic opportunity for our military to achieve a leapfrog development. Faced with these opportunities and challenges, there is an urgent need for forward-looking planning, strategic deployment, and comprehensive measures to seize the strategic high ground in future military competition and firmly grasp the strategic initiative in safeguarding national security and winning intelligent warfare.
Proactively design intelligent warfare. First-rate armies design warfare, second-rate armies respond to warfare, and third-rate armies follow warfare. Facing the impending intelligent warfare, we must anticipate and proactively design warfare as early as possible, aiming to transform from following, keeping pace, to leading, and strive to become visionaries and rule-makers of future warfare. First, we must focus on designing intelligent warfare from a technological perspective, enhancing our understanding of cutting-edge technologies, keenly grasping new trends in technological development, and identifying key areas, directions, and technologies that can trigger the evolution of warfare. We must design the initiative of warfare through technological advancement, the flexibility of warfare through technological integration, and the asymmetry of warfare through technological disruption. Second, we must focus on strengthening the development of new intelligent combat concepts, considering the future security threats facing my country and the missions undertaken by our military. Based on the development, application, and impact of military intelligence, we must focus on how to leverage intelligent warfare to overcome the war threats and strategic dilemmas facing my country. Around various strategic directions and new security fields, we must systematically envision the intelligent combat scenarios that may be faced in the future, vigorously promote innovation in intelligent combat theory, and accelerate the construction of an intelligent combat theory system with Chinese characteristics. Third, we should focus on strengthening the demand-driven development of intelligent warfare, focusing on new intelligent warfare styles, systematically describing the required capabilities, systems, and equipment, and using operational needs to drive the development of military intelligence, ensuring that operational needs are implemented in all aspects and throughout the entire process of military intelligence development, and comprehensively improving the combat effectiveness of military intelligence development.
Developing intelligent weaponry and equipment. Intelligent weaponry and equipment are the material foundation of intelligent warfare and an important symbol of an intelligent military. First, we must adhere to system construction. Information warfare is about systems, and intelligent warfare is even more about systems. Currently, intelligent weaponry and equipment, represented by intelligent command and control systems, intelligent drones, intelligent tanks, intelligent missiles, and intelligent landmines, are still in a stage of fragmented development and far from forming a systematic development. How to build an intelligent weaponry and equipment system, especially an intelligent network information system, has become a major strategic issue facing us. Second, we must adhere to a balanced approach of offense and defense. Where there is a spear, there will inevitably be a shield; where there is intelligent weaponry and equipment, there will inevitably be anti-intelligent weaponry and equipment. We must coordinate the development of offensive and defensive intelligent weaponry and equipment. For intelligent weaponry and equipment, once the enemy obtains the source code, it is equivalent to gaining the right to use the weapon. This places new and higher demands on the construction of intelligent weaponry and equipment that combines offense and defense. Third, we must coordinate the integrated development of mechanization, informatization, and intelligence. We must adhere to the principle of supporting intelligence with mechanization and informatization, and driving mechanization and informatization with intelligence. Through the coupling, proportional optimization, and system integration of elements of mechanization, informatization, and intelligence, we can accelerate the transformation, upgrading, and efficiency improvement of intelligent weaponry and equipment construction.
Shaping an intelligent organizational structure. Without the modernization of the military’s organizational structure, there can be no modernization of national defense and the armed forces. The fundamental function of the military’s organizational system is to ensure the effective integration of personnel and equipment, enabling the formation and continuous improvement of the military’s overall combat capability. To win intelligent wars and build an intelligent military, it is essential to establish an intelligent organizational system and construct an intelligent military force system. An intelligent military force system is an organic whole comprised of combat forces with intelligent weapon platforms as its backbone, organized according to human-machine collaboration and machine self-organization collaboration, conducting combat operations under authorized control or supervision by humans, as well as combat support forces providing reconnaissance, intelligence, communication, and algorithm design, and logistics and equipment support forces. Following the principles of “emphasizing coordinated development, focusing on competitive advantages, and promoting system integration,” and centering on expanding the scale and optimizing troop composition, while inheriting the traditional tree-like structure and service branch structure organizational models, a dual organizational system balancing stability and innovation should be established. Efforts should be made to construct a command system with a virtualized center of gravity, explore and innovate new organizational methods such as cross-domain mixed forces and manned/unmanned mixed formations, and strive to achieve the flexible, organic, and efficient operation of the intelligent military force system.
Strengthening Strategic Management of Intelligentization. The evolution of intelligent warfare begins with technology and is perfected through management. To meet the challenges of intelligent warfare and accelerate the development of military intelligence, we must prioritize strategic management, focusing on improving the quality and efficiency of military intelligence development and the operational efficiency of intelligent military systems. From a holistic perspective, we must strengthen overall planning, system design, centralized management, and categorized guidance, forging a path of intensive and efficient intelligent development. Adapting to the rapid response capabilities required by intelligent warfare, we must optimize management systems and mechanisms, adopting networked and autonomous management models. We must improve the planning and implementation of cutting-edge intelligent technology research and development and the transformation and application of scientific and technological achievements, increasing R&D investment and support to ensure that technological innovation remains at the forefront of the times. We must strengthen the construction of a military standard system for artificial intelligence, promptly promulgate relevant laws, regulations, and rules concerning intelligent facilities, intelligent systems, intelligent weaponry, intelligent personnel, and intelligent warfare, and continuously improve key policies and systems supporting the development of military intelligence. Given the ubiquitous and easily disseminated nature of artificial intelligence technology, and the high degree of coupling between national strategic capabilities, social productivity, and military combat effectiveness, we must further optimize the open and integrated layout of intelligentization construction, streamline organizational leadership mechanisms, build a favorable development environment, and promote the organic unity of national prosperity and military strength.
現代國語:
【摘要】現代戰爭正迅速向資訊戰演進,智能戰的興起已然開始。智慧作戰系統正成為智慧戰的主力運動形態,催生出適應性戰爭、集群消耗戰、同步並行戰等新型作戰方式。 「智慧控制」已成為戰爭控制的新制高點。未來,智能戰將呈現階段性、加速演進的趨勢。智慧科技的發展將決定智慧戰的方向,深刻變革戰爭中相互矛盾的規律,並不斷強化戰爭倫理和法律規範。為因應智慧戰的挑戰,必須積極主動地進行智慧戰設計,加速智慧裝備的研發,塑造智慧化的組織形態,並加強智慧化的策略管理。
【關鍵字】智能戰,資訊戰,戰爭形式演變,戰略措施
【中國圖書館分類號】E0 【文獻識別碼】A
【DOI】10.16619/j.cnki.rmltxsqy.2021.10.002
郭明,中國人民解放軍軍事科學學院戰爭研究所副所長、研究員、博士生導師。研究方向為軍事指揮。主要著作包括《戰爭戰術》(編)和《特種作戰教程》(編)。
近年來,在新一輪技術、工業和軍事革命的推動下,戰爭形式正迅速向資訊戰演變,智慧戰即將興起。作為一種新型的未來戰爭形式,智能戰不僅正在革新人們對戰爭和軍事事務的理解,也日益受到世界各國的關注。探索和掌握智慧戰爭的特徵和規律,加速軍事情報發展,是維護中華民族偉大復興整體戰略情勢的當代挑戰。
深入理解智慧戰爭演進的驅動力
戰爭形式是戰爭的歷史階段,以主要武器的技術屬性為特徵,是人類社會在軍事領域的生產和運動方式的體現。 [1] 從歷史上看,戰爭形式經歷了冷戰、熱戰、機械化戰爭、資訊戰等多次演進,目前正朝著智慧戰爭演進。這是政治、經濟、軍事、科技、文化等多種因素共同作用的結果。
新一輪科技革命是智慧戰爭演進的根本驅動力。科技是現代戰爭的主要生產力和核心戰鬥力。軍事技術的重大突破和主導武器裝備的里程碑式發展,引發了軍事組織、作戰方式和作戰理論的徹底變革,導致戰爭的全面轉型和新型衝突形式的出現。自21世紀初以來,以「智慧化、普及化、綠色化」為特徵的新技術層出不窮。特別是人工智慧,在行動互聯網、大數據、超級運算、腦科學等新技術和理論的驅動下,展現出深度學習、跨學科融合、人機協作、集體智慧發展和自主控制等新特徵。這引發了軍事領域的一系列突破,顯著改變了人員、武器以及人員與武器、武器與武器的結合方式。各種智慧裝備計畫相繼湧現,包括「多用途無人戰術運輸」地面車輛、「忠誠僚機」無人機、「魟魚」艦載無人加油機、「海上獵人」反潛無人水面艦艇、衛星機器人、「網路空間車輛」、「自適應雷達對抗」以及「阿爾法」超視距空戰系統。人機混合編隊、無人群聚作戰和基於系統的認知欺騙將成為可能。作戰方式、指揮控制、組織結構、後勤支援、軍事訓練等各領域都出現了系統性的重大創新。 「以情報控制能力」的智慧戰爭開始出現。
大國間的戰略競爭是智慧戰爭演進的驅動力。軍事從屬於政治,戰略從屬於政治戰略。毛澤東同志指出戰爭是「在特定發展階段,為解決階級、民族、國家和政治團體之間矛盾而採取的最高形式的鬥爭」。 [2] 大國間的戰略競爭及其所產生的軍事需求是推動戰爭演變的關鍵因素。二戰期間,儘管英國、法國、德國、美國和蘇聯的軍隊都擁有坦克、飛機和無線電通訊設備,但只有德國成功實施了「閃電戰」。一個非常重要的原因是,德國試圖利用閃電戰來打破兩線作戰的戰略困境。目前,世界正經歷百年未有之大變局,國際力量平衡正經歷近代以來最劇烈的變革,國際政治經濟格局正在發生深刻的調整。出於維護其世界霸權的戰略考量,美國提出了“第三次抵消戰略”,該戰略明確將人工智慧和自主性作為發展的兩大技術支柱。它從戰爭設計、作戰概念發展、技術研發和軍費開支等各方面加速軍事情報的發展,積極在軍事情報革命中搶佔先機,力求憑藉新的技術優勢獲得戰略主動權。俄羅斯堅持將有限的科技資源投入到具有高戰略價值、尖端技術和實用性的領域,並將情報視為武器裝備現代化的關鍵。俄羅斯已明確提出2025年將無人作戰系統的比例提高到30%。 [3] 英國、法國、印度和日本等其他大國也不甘示弱,紛紛加大對軍事情報的投入與部署。激烈的國際戰略競爭不僅影響各國軍事情報發展的戰略重點,也推動智慧戰的演進與發展。
軍事理論創新是推動智慧戰演進的思想先導,在軍事技術發展和戰爭演進中扮演重要的指導角色。人類戰爭史表明,尖端技術及其物質化武器要真正發揮作戰能力,必須以先進的軍事理論為指導。固守現有軍事理論而錯失建構和運用新型作戰能力的案例不勝枚舉。美軍始終強調從技術角度設計戰爭,透過發展新的作戰概念來推動國防技術、武器裝備和作戰能力的創新與飛躍。近年來美軍提出的新作戰概念均圍繞著「跨域協同」這一最高作戰概念。例如,美軍的「分散式作戰」透過「分散式」將各項能力解耦,再透過「協同」將其聚合,從而建構一個完整的作戰系統。這體現在兵力部署和運用上,意味著少量有人駕駛飛機與大量功能分解的智慧無人機協同作戰,形成一個完整的作戰系統。 2020年8月,美國國防高級研究計畫局(DARPA)組織了第三次人機空戰概念展示。在最終的虛擬對決中,人工智慧團隊取得了決定性的勝利。俄羅斯已明確將軍用機器人視為軍事情報發展的關鍵方向。今年4月,俄羅斯媒體揭露,其空天軍「閃電」多功能無人系統已完成集群部署測試,能夠執行俄軍「集群」作戰概念的攻擊任務。 [4] 這些已具備一定智慧特質的作戰概念的核心在於探索如何透過提升「智慧」來協調各軍事力量的運用,從而憑藉跨域非對稱優勢擊敗對手並取得全面勝利。智慧戰的形成依賴於對智慧技術的深刻理解、對其軍事應用潛力的敏銳洞察,以及戰爭藝術與智慧技術創新和智慧軍事理論發展的高度融合。
探索實戰是推動智能戰演進的首要途徑。戰爭的演變是一個動態過程;每一種戰爭形式都會經歷一個從數量變化到質量變化的過程。漸進式變革最終會導致突發式變革。與資訊戰的興起相比,智能戰目前尚缺乏像海灣戰爭那樣完整且典型的實戰案例。然而,智慧戰領域的實驗和實踐正推動智慧戰從萌芽階段發展到雛形階段,再從早期階段邁向高階階段。 2015年,俄羅斯在敘利亞戰爭中首次系統性地部署了四台履帶式「平台-M」戰鬥機器人和兩台輪式「阿爾戈」戰鬥機器人,並配合無人偵察機和「仙女座-D」自動化指揮系統,開創了以戰鬥機器人為主的地面作戰先河。 2018年1月,俄羅斯軍隊首次在敘利亞戰場使用反情報設備,摧毀、幹擾並捕獲了13架來襲無人機。 2019年9月,十幾架無人機襲擊了沙烏地阿拉伯的兩處石油設施,導致其石油產量減半。在2020年納戈爾諾-卡拉巴赫衝突中,阿塞拜疆軍隊進攻亞美尼亞軍隊期間,無人作戰平台的使用率首次超過有人作戰平台,達到75%以上。無人機的使用數量、頻率和強度均創人類戰爭史新高。 [5] 這些在智慧戰領域的實踐探索,不僅將推動智慧裝備在戰場上更廣泛地應用、部署更多種類、應對更複雜的作戰場景,還將促進對抗中智能戰方法和反智能戰方法的逐步升級,從而加速智能戰的深刻演進。
準確掌握智能戰的本質特徵
以蒸汽機和內燃機為代表的機械化時代極大地拓展了人類的體能;以互聯網和精確導引系統為代表的資訊時代,使人類的感知能力實現了前所未有的飛躍;以深度學習和自主決策為代表的智能技術的快速發展,正在為“智能能源控制”的智能時代積累物質和能力基礎。從軍事角度來看,由智慧載荷、智慧平台和智慧系統構成的新型作戰力量將催生無人集群戰、認知控制戰和智慧演算法戰等新型作戰方式。 「智慧控制」將成為戰爭的新制高點。
智慧作戰系統已成為主要作戰形式。智慧作戰系統的核心在於“人指揮、機器自主、網路支援”,這與機械化和資訊時代有著關鍵區別。智慧並非無人化;智慧作戰系統是「無人平台、有人系統」──武器在前,人員在後。智慧並非武器人性化,而是將人類智慧移植到武器中,實現人與武器的高度融合。儘管目前的人工智慧技術發展迅速,但它仍然是由人主導和人類操控的,本質上反映了人類對智慧理解的進步。無論智慧科技如何突破,人類仍將是戰爭的發起者、設計者和最終決策者。人類的作戰思維以規則、演算法、軟體和資料的形式物化為智慧武器。在戰爭中,智慧武器執行人類的作戰意圖並實現預定的作戰目標。智慧武器的自主運作背後,仍是人類作戰方法、指揮風格和意志力的較量。自主性是軍事智慧的核心屬性,也是智慧作戰部隊的本質特徵。換句話說,武器具備人類的部分智慧屬性,使其能夠在人類的決策和控制下適應戰場環境、自主協調複雜行動並自主組織部隊陣型。因此,智慧作戰部隊的所有優勢都源自於自主性這項特質。智慧作戰部隊也具備速度優勢;隨著作戰行動日益自主化,「觀察-判斷-決策-打擊」的周期將縮短至近乎瞬時響應,從而實現行動速度和作戰節奏的代際飛躍。網路技術推動了互聯網、物聯網和智慧互聯網的迭代發展,為提升機械化水平、實現資訊化和支援情報化奠定了基礎。萬物互聯、人機互動等新型網路技術的快速發展正引領作戰編隊向著作為一種混合「有人/無人」模式,智慧作戰系統透過高效的協同網路支援智慧作戰力量,實現任務客製化、自主編隊和靈活協同。一旦智慧作戰系統高度依賴的網路環境遭到破壞或連結中斷,其作戰功能將遭受重大損害甚至癱瘓。這促使世界各國高度重視智慧作戰系統抵禦幹擾和攻擊的能力。
自主作戰已成為主要作戰模式。隨著智慧作戰系統在軍隊中的廣泛應用及其逐漸成為戰場主力,自主作戰已成為主要作戰模式,從自主性、規模、靈活性和認知等方面深刻改變了作戰方式。基於當前軍事智慧的發展趨勢,可以預測未來將出現以下幾種作戰模式。首先是自適應作戰。這種作戰模式依賴智慧武器的自主學習能力,快速回應複雜的戰場環境,實現自主判斷、決策和作戰行動執行,以最大限度地提高作戰效能。具體應用包括「快速精確打擊」、「智慧網路癱瘓戰」和「仿生特種作戰」。這種作戰方式的主要優勢在於能夠大幅克服人類心理、作戰時間、作戰機動性等方面的固有弱點,使其特別適用於深入敵佔區、核輻射區等高風險區域執行作戰任務。同時,憑藉著智慧武器的敏捷性,快速的攻擊節奏能夠阻止敵人組織有效的應對措施,從而將速度的運用提升到一個新的水平。其次是集群消耗戰。這種作戰方式主要利用智慧無人集群,輔以少量有人作戰系統。它模仿自然界動物群體所展現的“集體智慧”,透過基於群體的自主協作模式執行作戰任務。具體應用包括「蜂群戰」、「魚群戰」和「狼群戰」。這種作戰方式的主要優勢在於利用低成本、小型智慧武器,透過飽和攻擊或自殺式攻擊摧毀高價值敵方目標,從而將數量優勢轉化為對傳統大型主戰平台的不對稱系統優勢。第三種是同步並行作戰。這種作戰方式將作戰功能分解為部署在整個作戰域的多個異質小型有人和無人作戰平台。透過在這些平台之間建立分散式通訊網絡,實現作戰在時間、空間和層級上的同步,從而能夠系統地完成作戰任務。這種作戰方式的主要優點在於利用智慧網絡,將智慧感測器、作戰平台和單兵系統廣泛分佈,進行同步並行打擊,奪取作戰優勢。
「情報優勢」已成為戰爭的核心。戰爭優勢的發展與戰爭本身的演變一致。火力和機動性是機械化戰爭中取得勝利的關鍵因素,陸海空優勢成為爭奪優勢的核心。資訊力量是資訊化戰爭中致勝的關鍵因素,空間和資訊優勢成為爭奪主導權的核心。智慧優勢是智慧戰爭中致勝的關鍵因素,「智能主導」成為爭奪主導權的核心。智慧主導、自主能源控制和以智慧取勝將成為智慧戰爭的基本原則。 「智能主導」的爭奪本質上是「演算法+資料+認知」的綜合較量。演算法是智慧技術的核心;「演算法即戰術,軟體定義戰爭」已成為智慧戰爭的顯著特徵。演算法建構的核心是基於問題創建抽像模型,並根據目標問題選擇不同的方法完成演算法設計。擁有演算法優勢的一方可以精確模擬作戰場景,準確評估作戰結果,並最大限度地推導出最優作戰方案,從而在戰鬥開始前就擁有製勝的強大手段。 「誰擁有最先進的演算法誰就佔優勢」已成為新的戰爭法則。在智慧時代,數據是許多顛覆性技術的核心資源。在智慧戰爭中,掌握、分析和爭奪數據並將其應用於戰爭,已成為取得勝利的關鍵。智慧武器具備某些人類智力特徵,使得認知領域成為衝突的焦點。透過智慧技術,針對認知迴路,限制敵方獲取有效訊息,迫使其使用錯誤訊息,延緩其認知速度,誘導其認知模式,並阻斷其認知輸出,可以擾亂敵方的指揮和決策,打擊其士氣,從而實現對「贏得民心」這一古老戰爭法則的可定制化和可控應用。在資訊戰中,失去資訊控制的一方,即使其人員和平台可能未被摧毀,也會失去順暢的溝通,無法形成一個有機的整體。在智慧戰爭中,即使擁有資訊和能源優勢,如果沒有智慧優勢,人機協調的喪失和自主決策的失敗也會導致整體作戰效能的顯著下降。
智能化並未改變戰爭的本質。葉劍英元帥指出,「戰爭有兩種方式:一是政治,二是技術。政治決定戰爭的本質,技術決定戰爭的方式」[6]。智慧戰爭並未顛覆馬克思主義戰爭理論的基本原則,但其基本範圍將出現許多新的發展和變化。一方面,智慧戰爭的政治決定性並未改變,它仍是政治的工具。政治決定戰爭的動機、目的和本質。如果戰爭的目的沒有政治的確定,戰爭就變成了盲目的殺戮,戰爭失去了靈魂。在當今時代,霸權主義和強權政治仍然是戰爭的主要根源。民族和宗教矛盾、能源資源競爭、領土主權和海洋權益爭端仍將是戰爭的直接原因。無人自主系統的廣泛應用模糊了戰爭與非戰爭的界線。戰略和軍事風險的降低可能導致未來戰爭門檻的降低。尤其值得注意的是,智慧科技的雙重用途特性以及眾包、眾籌、創客計畫等「開源共享」模式的廣泛應用,使得裝備和技術的獲取日益商業化。這將深刻改變智慧時代戰爭的主要參與者,導致戰爭行為體更加多元化,其中非國家行為者特別突出。另一方面,決定智慧戰爭勝負的政治因素依然不變,仍取決於戰爭本身的本質。促進歷史進步並反映社會大多數人政治目標的戰爭是正義戰爭;反之,則為非正義戰爭。正義戰爭必勝、人民是勝利基石的原則,仍將是智慧戰爭時代勝利的鐵律。然而,隨著智慧科技催生智慧社會,公眾在智慧戰爭中的角色和地位將被重新定義,公眾參與的廣度和深度將顯著提升。公眾將日益成為攻擊的直接目標、防禦的主力軍以及智慧戰爭的強大後盾。因此,必須辯證、全面地審視智能戰,避免純粹的軍事或技術視角,認識到智能戰的“變化”與“不變”,從而探索智能戰的製勝之道。
智慧戰發展趨勢的科學預測
目前,智能戰仍處於起步階段。預測智能戰的發展趨勢既必要又具有挑戰性。一些學者指出,雖然我們可以大致判斷機器學習、工業機器人、材料科學等技術的未來發展趨勢,但我們無法準確預測這些技術將如何融合,以及它們將對未來戰爭產生何種具體影響。 [7] 這就要求我們摒棄從單一技術出發的思維模式,並著眼於理解智能戰整體可能的發展趨勢。
智能戰將分階段演進。隨著現代科技呈指數級、整合式和數據驅動式發展,以及在軍事領域的加速轉型應用,武器裝備的轉型升級進程也不斷縮短。此外,世界目前正處於大發展、大變革和大調整時期。區域動盪和局部戰爭將成為常態,情報探索也將日益頻繁。智慧作戰實踐將日益頻繁,所有這些都將促進智慧戰爭的加速發展。同時,由於智慧科技發展、智慧力量融入作戰體系、軍事觀點更新等主客觀條件的限制,智慧戰爭的演進將呈現明顯的階段性。一些學者提出,要真正進入智慧戰爭階段,人工智慧技術需要達到四個層次,即計算智能、感知智能、認知智能和人機融合增強智能。當人工智慧技術達到第二層次時,智慧戰爭將開始;當達到第四層次時,智慧戰爭時代將全面開啟。 [8] 基於此,可以初步判斷,未來15年左右將出現較為典型的智慧戰爭,未來30年內智能戰爭可能成為戰爭的基本形式。實踐表明,軍事領域的每一次變革和戰爭形式的每一次演進都源於新型作戰力量的出現。新型作戰力量憑藉著獨特而先進的軍事技術,具有「王牌」性質,往往能夠打破戰場上的力量平衡,成為決定勝負的關鍵力量。一旦這些新型作戰力量融入作戰體系並在實戰中大規模部署,就標誌著戰爭性質的根本性轉變。智慧戰爭的真正出現,必然是智慧無人作戰平台、智慧無人作戰集群等新型作戰力量發展壯大並融入現有作戰體系的結果。這是一個循序漸進、不斷深化的長期過程,從初步融合到深度融合並非一朝一夕之功。
智慧技術的發展將決定智慧戰爭的方向。智慧技術是一門綜合發展與運用腦與認知、生物交叉、先進計算、大數據、微納技術等尖端技術,研究智慧行為機制及其實現方式的科學技術。作為智慧戰爭演進的根本驅動力和物質基礎,人工智慧的發展趨勢、產業基礎、技術成熟度以及在軍事領域的應用深度和廣度直接決定智慧戰爭的未來發展方向。人工智慧技術在60多年的發展歷程中經歷了三次崛起和兩次衰落。目前,人工智慧的發展仍處於統計學習的早期階段,並且可能在很長一段時間內都停留在弱人工智慧階段。能夠獨立於人類演進的強人工智慧,短期內難以實現。智慧科技的發展與突破直接決定智慧化是資訊化的更高階段,還是超越資訊化的更高階段。目前,智慧科技發展對智慧戰爭的驅動力主要集中在以下幾個面向:首先,智慧科技賦能現有武器裝備。雖然目前發展主要集中於針對特定應用場景的專用智慧系統,但它已經不斷提升了航空母艦、飛機等傳統主戰平台的作戰效能,逐步從直接由人類操控發展到能夠自主完成特定作戰任務。其次,智慧技術正在改變未來的作戰指揮模式。智慧技術對指揮控制系統的整合與改造將促進指揮實體的混合化、指揮結構的彈性與指揮模式的敏捷性。作戰層面上對適應性、自組織性和自協調性指揮優勢的競爭將更加激烈。第三,智慧科技正在更新未來的作戰流程。智慧技術將陸、海、空、天等多個作戰領域的多條殺傷鏈融合整合為跨域殺傷網絡,從根本上改變傳統的「從感測器到射手」的單一作戰流程。
智慧戰爭中的矛盾規律將會發生深刻變化。運用戰爭中的矛盾規律是理解戰爭規律的主要途徑,而交戰雙方的對抗是戰爭的根本矛盾。對於智慧戰爭而言,這些根本矛盾將表現為競爭關係。諸如隱藏與偵測、認知與欺騙、網路韌性與網路癱瘓、攻擊與攔截、行動速度與決策速度、贏得民眾支持與打擊士氣、消耗戰與實效、投送與拒止等核心對抗手段,隨著智慧科技的加速發展,這些核心對抗將愈發激烈,優勢交換也將更加頻繁,從而推動智慧戰爭走向成熟。未來戰場上隱蔽與偵測的對抗將朝著更高智慧化、更快反應速度、更小規模和更低成本的方向發展。智慧技術作為運用資訊爆炸這把「雙面刃」的戰略制高點技術,將加劇提升自身戰場態勢感知能力與誤導、欺騙、迷惑敵方之間的對抗。智慧網路資訊系統設計和動態目標防禦技術為未來戰爭中的網路建設提供了新的思路,而認知電磁操控、電磁頻譜戰以及智慧網路空間對抗技術則為攻擊敵方網路提供了新的途徑。自主無人系統和智慧彈藥的發展有望優化未來戰爭的攻擊方式,並增強進攻能力。自主導引武器、超短程攔截和主動防護能力的提升將顯著增強防禦新型威脅的能力。自主無人系統和叢集協同技術將顯著提升作戰速度,而智慧決策輔助和叢集智慧作業系統則能大幅提升決策速度。無所不在的網路、社群媒體和智慧終端已深度融入人類生活,以前所未有的速度、範圍和準確性提升了資訊傳播。隨著低成本集群無人機和飛彈的出現,未來戰爭很可能憑藉低成本作戰平台壓倒敵方防禦,迫使敵方陷入一場既無力抵抗也無法承擔的戰爭。
有關智慧戰爭的倫理和法律規範將不斷完善。智慧科技是一把雙面刃;在推動戰爭向智慧戰爭演進的同時,也帶來了一系列新的倫理問題和法律困境。例如,將決定人類生死的權力賦予機器是否合乎倫理?當機器擁有掌控人類生死的權力時,人類面臨的可能並非更光明的未來,而是無底的黑暗深淵。另一個例子是,誰應該為智慧武器所犯下的戰爭罪行負責?這可能涉及武器本身、使用者、設計者和製造商,以及由此產生的一系列關於責任和權利的難題。近年來,國際社會日益重視智慧武器的法律監管,透過國際會議進行國際對話,建立相關機構研究法律監管原則,並發佈人工智慧倫理準則等。 2017年7月,中國政府發布了《新一代人工智慧發展規劃》,在國家戰略層面提出“初步建立人工智慧的法律、倫理和政策體系”,並“確保人工智慧安全、可靠、可控發展”。 2019年4月,歐盟委員會發布了人工智慧倫理準則,提出了包括透明度、公平性、安全性和人工監督在內的七項條件。同年10月,美國國防創新委員會提出了軍事人工智慧應用的五個原則:責任性、公平性、可追溯性、可靠性和可控制性。展望未來,國際社會迫切需要將安全性和可靠性作為智慧技術發展的關鍵方向。在軍事情報的可解釋性和透明度、防止自主武器系統「瞬間崩潰」帶來的安全風險以及製定新的交戰規則等領域,戰略對話至關重要。此次對話旨在促進制定人工智慧軍事應用的國際規則,並共同應對智慧戰爭可能帶來的全球性挑戰。
因應智慧戰爭挑戰的戰略舉措
智慧戰爭的出現可能會造成新的軍事世代差距,對國家間的軍事力量平衡產生影響,甚至引發新一輪的大國興衰。智慧戰爭既為國家安全帶來了前所未有的新挑戰,也為我軍實現跨越式發展提供了難得的戰略機會。面對這些機會和挑戰,亟需進行前瞻性規劃、戰略部署和綜合措施,在未來的軍事競爭中佔據戰略制高點,牢牢掌握維護國家安全和贏得智慧戰爭的戰略主動權。
主動設計智慧戰爭。一流軍隊設計戰爭,二流軍隊應對戰爭,三流軍隊跟隨戰爭。面對即將到來的智慧戰爭,我們必須儘早預判並主動設計戰爭,力爭從跟隨、並駕齊驅轉變為引領,努力成為未來戰爭的先行者和規則制定者。首先,我們必須從技術角度出發,著力設計智慧戰爭,加深對尖端技術的理解,敏銳掌握技術發展的新趨勢,辨識能夠引發戰爭演進的關鍵領域、方向和技術。我們必須透過科技進步來設計戰爭的主動性,透過科技融合來設計戰爭的彈性,透過科技顛覆來設計戰爭的非對稱性。其次,我們必須著重加強新型智慧作戰概念的研發,結合我國未來面臨的安全威脅和軍隊的任務,在軍事情報發展、應用和影響的基礎上,重點研究如何利用智慧作戰來應對我國面臨的戰爭威脅和戰略困境。圍繞著不同的戰略方向和新的安全領域,我們必須有系統地構想未來可能面臨的智慧作戰場景,大力推動智慧作戰理論創新,加速建構具有中國特色的智慧作戰理論體系。第三,我們應該著重加強智慧作戰需求驅動型發展,聚焦新型智慧作戰模式,系統地描述所需的能力、系統和裝備,以作戰需求為導向,推動軍事情報發展,確保作戰需求在軍事情報發展的各個面向和整個過程中得到貫徹落實,全面提升軍事情報發展的作戰效能。
研發智慧武器裝備。智慧武器裝備是智慧戰爭的物質基礎,也是智慧軍隊的重要像徵。首先,必須堅持系統化建設。資訊戰的核心在於系統,而智慧戰爭更是如此。目前,以智慧指揮控制系統、智慧無人機、智慧坦克、智慧飛彈、智慧地雷等為代表的智慧武器裝備仍處於分散發展階段,距離系統化發展還很遠。如何建構智慧武器裝備系統,特別是智慧網路資訊系統,已成為我們面臨的重大戰略問題。其次,必須堅持攻守平衡發展。有矛必有盾,有智慧武器裝備必有反智能武器裝備。必須協調發展攻防兼備的智慧武器裝備。對於智慧武器裝備而言,一旦敵方取得了原始碼,就相當於獲得了使用該武器的權利。這就對攻防兼備的智慧武器裝備建設提出了新的更高要求。第三,要協調機械化、資訊化和智慧化的一體化發展。要堅持以機械化和資訊化支撐智能化,以智慧化驅動機械化和資訊化的原則。透過機械化、資訊化和智慧化各要素的耦合、比例優化和系統集成,可以加速智慧武器裝備建設的轉型升級和效率提升。
建構智能化的組織結構。沒有軍隊組織結構的現代化,就沒有國防和軍隊的現代化。軍隊組織體系的根本功能是確保人員和裝備的有效整合,從而形成和不斷提升軍隊的整體作戰能力。打贏智慧戰爭,建構智慧化的軍隊。對於精銳軍隊而言,建立智慧組織體系、建構智慧化軍事力量體系至關重要。智慧化軍事力量體係是一個有機整體,由以智慧武器平台為骨幹的作戰力量、按照人機協同和機器自組織協同原則組織起來的作戰力量、在人類授權控製或監督下開展作戰行動的作戰支援力量以及提供偵察、情報、通信和演算法設計的作戰支援力量和後勤裝備支援力量組成。應遵循「強調協同發展、聚焦競爭優勢、推進系統整合」的原則,以擴大規模、優化部隊構成為核心,在繼承傳統樹狀結構和兵種結構組織模式的基礎上,建構穩中創新並重的雙軌組織體系。應努力建構重心虛擬化的指揮體系,探索創新跨域混合部隊、有人/無人混合編隊等新型組織方式,力求實現智慧化軍事力量體系的靈活、有機、高效運作。
加強智能化策略管理。智能戰的演進始於技術,終於管理。為因應智慧戰的挑戰,加速軍事情報發展,必須優先發展戰略管理,並專注於提升軍事情報發展的品質和效率,以及智慧軍事系統的作戰效能。若要從整體加強統籌規劃、系統設計、集中管理和分類指導,打造密集、高效的智慧發展道路。要適應智慧戰對快速反應能力的要求,優化管理體系和機制,採用網路化、自主化的管理模式。要完善前沿智慧技術研發與科技成果轉換應用的規劃與實施,加大研發投入與支持力度,確保技術創新始終處於時代前沿。要加強人工智慧軍事標準體系建設,及時頒布智慧設施、智慧系統、智慧武器、智慧人員和智慧戰的法律法規,不斷完善支持軍事情報發展的關鍵政策和製度。鑑於人工智慧技術的普及性和易傳播性,以及國家戰略能力、社會生產力和軍事作戰效能之間的高度耦合性,我們必須進一步優化智能化建設的開放一體化佈局,精簡組織領導機制,營造良好的發展環境,促進國家繁榮與軍事實力的有機統一。
注释
[1]《中国军事百科全书·战略》(第二版),北京:中国大百科全书出版社,2014年,第506页。
[2]《毛泽东选集》第1卷,北京:人民出版社,1991年,第171页。
[3]赵林:《从空中、地面到水下无人作战系统——无人作战,俄军走了多远》,《解放军报》,2019年1月31日第11版。
[4]陈梓毅、饶雨峰、马建光:《“闪电”无人机或成俄空天军未来作战新秀》,2020年4月16日,人民网,http://military.people.com.cn/n1/2021/0416/c1011-32079848.html。
[5]兰顺正:《纳卡冲突中的现代武器及战术比拼》,《世界知识》,2020年第24期。
[6]《叶剑英军事文选》,北京:解放军出版社,1996年,第250页。
[7]傅莹:《看世界2》,北京:中信出版社,2021年,第292页。
[8]李始江、杨子明、陈分有:《以新理念迎接智能化战争挑战》,《解放军报》,2018年7月26日,第7版。
2021-08-11 15:xx 来源: 《人民论坛·学术前沿》2021年5月下 作者: 郭明
中國原創軍事資源:https://www.rmlt.com.cn/2021/0811/68281848089.shtml